Chapter 4__2_1_Human Population Growth
advertisement
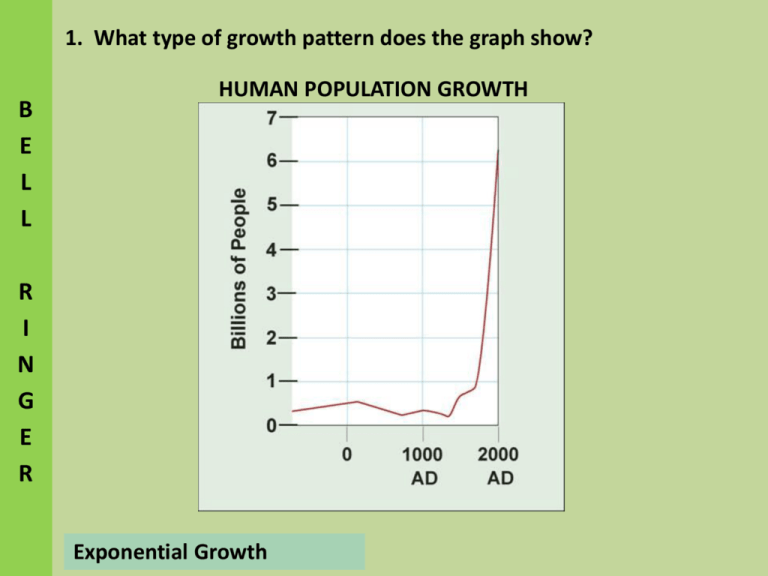
1. What type of growth pattern does the graph show? B E L L HUMAN POPULATION GROWTH R I N G E R Exponential Growth HUMAN POPULATION GROWTH Objectives: • Identify how the birthrate and death rate affect the rate at which a population changes. • Compare the age structure of rapidly growing, slow-growing, and no-growth countries. HUMAN POPULATION GROWTH Historical Overview Like the populations of many other living organisms, the size of the human population tends to increase with time. For most of human existence, the population grew slowly Limiting factors (competition, disease, parasitism, and natural disasters) kept population sizes low. About 500 years ago, the human population began growing more rapidly due to easier and safer advances in agriculture and industry. Death rates were dramatically reduced due to improved sanitation, medicine, and healthcare, while birthrates remained high. PATTERN OF HUMAN POPULATION GROWTH Human Population Growth 1. The size of the human population began to increase exponentially after the a. bubonic plague. b. development of plowing and irrigation. c. Industrial Revolution. d. development of the first cities. 2. Which of the following is NOT a potential limiting factor of human population growth? a. famine b. medicine c. war d. disease Factors that help Predict Patterns of Human Population Growth • Birthrates • Death rates • Doubling time • Age structure of a population Birthrate is the number of live births per 1000 population in a given year. Death rate is the number of deaths per 1000 population in a given year. Population Growth Rate (PGR) = Birthrate – Death rate Doubling time is the time needed for a population to double in size. Demography: The study of human populations that examines the characteristics of human populations and attempts to explain how those populations will change over time. Demographic Transition: A dramatic change in birth and death rates. Stage 1: High death rates and high birthrates. Stage 2: Death rate drops, while the birthrate remains high (the population increases rapidly). Stage 3: Birthrate decreases, causing population growth to slow. The demographic transition is complete when the birthrate falls to meet the death rate, and population growth stops. 3. After the demographic transition is complete, a population a. grows rapidly. b. grows slowly. c. begins a period of rapid decline. d. stays about the same size as time passes. Age Structure: how many people of different ages make up a given population. • Demographers can predict future growth using models called agestructure diagrams. Age-structure diagrams show the population of a country broken down by gender and age group. 4. An age-structure diagram shows a breakdown of a population by a. location and age group. b. age group and gender. c. birthrate and death rate. d. age group and emigration rate.