Population Geography - geography-bbs
advertisement
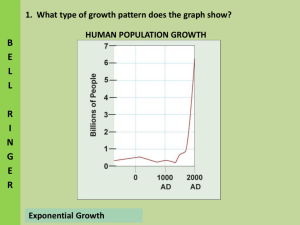
Demographics: Population Geography Population Geography OBJECTIVES: How is the world’s population distributed, and why? Why has the world’s population grown over time? What factors will affect the size of future populations? Global Population Density Demography- the study of the human population that emphasizes statistics (facts/figures); used to compare population distribution, population density, trends in population Geography of human population is uneven Some regions densely populated; others not Some area have aging populations; other areas mostly children Why do some areas of the world have fewer people? Harsh climate Farming is difficult Population Density: the average number of people living in an area; usually expressed as persons per square mile/kilometer World Population Density Map Why do some areas of the world have a more dense population? Environments favorable to farming Industrialized cities Pleasant climates 4 large regions of dense human settlement: eastern China, south Asia (India and Bangladesh), western Europe, eastern North America Population Growth End of last Ice Age= less than 10 million 2000 years ago= 250 million people 1650 A.D.= 500 million people 1850 A.D.= 1 billion people 1940 A.D.= 2 billion people 1975 A.D.= 4 billion people 2000 A.D.= 7 billion people •10,000 B.C. Introduction of Agriculture •World population has declined only in times of widespread disease/war/natural disasters Recap What is demography? What is population density and how do we we examine it? What factors contribute to the population density of a given location? Provide at least 3 factors. How the Population Grows Birthrate- the number of births per 1,000 people in a given year Death rate- the number of deaths per 1,000 people in a given year If birthrate exceeds death rates= population increases If death rate exceeds birth rates= population decreases As a country’s economy develops there are 3 stages of population growth. 1st Stage of Demographic Transition Birthrate and death rate are high but equal Many births but widespread disease causes many deaths 2nd Stage of Demographic Transition Death rate declines steadily while the birthrate remains high Family size increase; more children survive to adulthood Health care and safe water become more widespread 3rd Stage of Demographic Transition Birthrate drops and most children live to adulthood Family sizes decrease as more people decide to have fewer children Birthrate and death rate become about the same, though at lower levels Rate of population growth again become low Population is still much higher than in the first stage Push and Pull Factors Push factor- something that pushes someone to leave a country (religious persecution) Pull factor- something that pulls a person to immigrate to a new country (better wages) Emigrant- someone who moves out of a country Immigrant- someone who moves into a country Rate of Natural Increase Natural Increase- this rate is based on just births and deaths; it does not take migration into account. Rate is found by subtracting the death rate (Y) from the birthrate (X) (Hence: XY= Z (rate of natural increase- expressed as a percentage) Rate of Natural Increase Highest rates of Natural Increase? Africa, Southwest Asia (can be 3% or higher) Moderate rates of Natural Increase? Central, South America and Southeast Asia (1-3%) Low rates of Natural Increase? Europe and North American Countries, Japan, Australia, New Zealand (<1%) Negative rates of Natural Increase? Italy, Russia Population change/Economic success Developed countries= period of rapid population growth has slowed/low birthrates and low death rates Developing countries= have not completed the three stages of population growth; birthrates still exceed death rates What’s the Explanation? What is the reason that some nations Why does Africa and Southwest Asia have such high rates? What stage of demographic transfer are they in and why? Give at least 3 reasons. Why does Italy and Russia have such negative rates? What stage of demographic transfer are they in and why? Give at least 3 reasons. Homework You are going to identify 8 countries (4 pairs) and then highlight in what ways these countries are both similar and different in terms of demographics. For instance: countries might resemble in terms of population but vary in terms of economic condition. I want you to find different examples of this. Once you have identified the nation’s similarities and differences I want you to explain in a paragraph why you believe such differences exist. For example why would two nations with the same/similar population densities have different economic predicaments? Some areas to compare are: population density, urban vs rural development, ethnicity, education level, health measures, economic state, religion