wg 5.11
advertisement

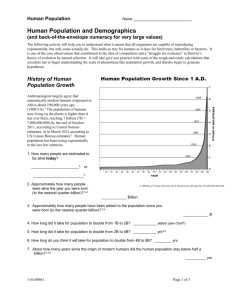
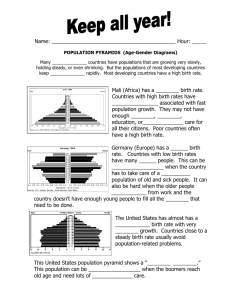
Chapter 5 Section 1 World Geography Population Geography Pg. 87 Studying Population Study the relationships between populations and the environment. Demography – the statistical study of human populations. Use these numbers to forecast what the population will be like in the future. Population Density The average number of people living in an area. Persons per square mile. You can tell how large a country is, or discover what areas they live in. Population Distribution About 90% of the world’s people live in the Northern Hemisphere. Lowland areas are heavily populated. People tend to live in areas that are favorable for settlement. Population Change The number of people in an area are a result of these 3 factors: – Birthrate – number of birth per 1,000 in one year. – Death rate – number of deaths per 1,000 per year. – Migration – people moving from one place to another. Migration Geographers – study migration by analyzing push factors and pull factors. Push factors are what causes people to leave one place. Pull factors – attracts people to a location. Natural Increase Rate of natural population growth. Number of birth and deaths in a year. Highest rates of increase are found in Africa and Southwest Asia. Lowest rates of increase are in Europe and North America. World Population Trends Number of people is increasing by 80 million per year. Some worry about overpopulation. This exists when the number of people is too large to be supported by available resources. No one knows for sure how many people the world can support. The Demographic Transition A model that shows how birthrates and death rates dropped in many western countries as they developed modern economies. Most of the world’s richest and technological advanced countries have had their birthrates drop. Future Populations Population projections are estimates of a future population’s size, age, growth rate, or other characteristics based on current data. All countries will face population-related challenges. Ex: caring for growing number of children or older people.