File
advertisement
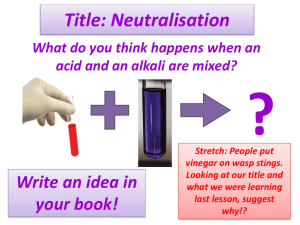
CKS3: Yr7 Chemistry Unit 1 – Me the the Scientist! Lesson number: 6. Lesson Title: Neutralisation Learning Outcomes How I did Learning Outcome 1: Understand what are neutralisation reactions. Level 5 I am working at I can move up to Connector: level .....because level…... by .............................. ……………………… ........................ ………………… Recall: Complete the quiz on the next slide. I am working at I can move up to level .....because level…... by .............................. ……………………… ........................ ………………… Learning Outcome 2: Plan an experiment to test how effective different antacids are. Level 6 Learning Outcome 3: Use your knowledge to explain everyday applications of neutralisation Level 7 I am working at level .....because .............................. ........................ Targets I can move up to level…... by ……………………… ………………… 11:30 Quiz on acids and alkalis •Acid, alkali or both??? 1) This has a pH of less than 7 2) This could kill cells 3) This is often used in cleaners or soap 4) This would turn Universal Indicator red 5) Sodium hydroxide is a common ____________ 6) This would feel soapy on your skin 7) This could be a corrosive 8) This will turn universal indicator purple 9) This would taste sour 10) Lemon juice and vinegar are examples of weak _____ Extended Learning • Research information and Collect Secondary data on: • Write a page of A4 explaining your understanding of acids and alkalis, neutralisation, chemical reactions, word equations and anything thing else you have learnt during this unit. • Due date: • Next lesson • Research Report Criteria (6 marks total = Level 7): • 1) Range of different reliable sources used and references included (books/internet/survey etc), • 2) Information written in own words • 3) Clear and logical structure to research report including pictures/diagrams which have been referenced • 4) No evidence of copy and paste! 11:30 BIG picture Key Question: • What skills will you be developing this lesson? • Scientific Investigation skills- by Research and Collecting Secondary data, Planning and Collecting primary data, Analysis and Evaluation. • Numeracy- by using formulae in calculations • Literacy- by writing well structured sentences and paragraphs • ICT- by using Laptops and electronic resources • Personal skills- team work, leadership • Thinking and Learning skills- organisation, logic, participation, memory, exploration, creativity, judgement, planning, practice. • Reflection- through self or peer assessment of each Learning Outcome •How is this lesson relevant to every day life? •Useful acid and alkali reactions are applied in food preservation, soil treatment, hair and skin care and bee stings •Quick Discussion: •What do you already know? 11:30 Keywords: • Neutralisation • Acid • Alkali • Neutral • Indicator • Antacid • Universal indicator • Variables Here are some of the words we will be using this lesson… 1) Create sentences which use the keywords correctly. 2) Put your hand up if there is any key word from the list that you don’t know the meaning of. 11:30 New Information for Learning Outcome 1 Explore and Discover: • Visual: Demonstration - What is neutralization? •The chemical reaction between an acid and an alkali •is called neutralization. acid alkali a salt water •What happens to the pH value of the reaction mixture during neutralization? •The pH value of the reaction mixture becomes closer to 7. • Audio: • Kinaesthetic: 11:30 11:30 Neutralisation •Something that is not an acid or an alkali is said to be NEUTRAL •Water is an example of a NEUTRAL SOLUTION •An acid and alkali will neutralise each other if the correct amounts are used: •Acid + alkali Salt + water •E.g. hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide sodium chloride + water 11:30 Learning Activities for Outcome 1 Worksheet 4.6.1 or Rainbow fizz • Predict what will happen after you read the method • Carry out experiment to see what happens when you add acids and alkalis together • Record Results Extension: 1. Explain why the colours changed. 2. Does the reaction have a name? 3. Can you write a word equation to describe the reaction? 11:30 11:30 Demonstrate your Learning for Outcome 1 Keywords: •Neutralisation • Acid Create • Alkali • Neutral Evaluate Apply (L5) Can you explain why the colours changed Can you write a word equation for the reaction? 11:30 Which task(s) will you Analyseto choose complete? Try to target a Apply level higher than your current level. Understand Remember • Indicator Understand (L4) Have recorded you observations correctly Learning Outcome 1: Review Go back to your Learning Outcome grid and fill out the ‘How I did’ and the ‘Targets’ column. Learning Outcome How I did Targets I am working at level .....because ........................... ........................... I can move up to level…... by …………………… …………………… Learning Outcome 1: Level 5 11:30 New Information for Learning Outcome 2 Explore and Discover: Antacids: •Are usually alkaline and are used to neutralize stomach acid 11:30 Learning Activities for Outcome 2 • What is the general word equation for neutralisation? • Plan an experiment to test which antacid is best Extension • What is your prediction and why? • What are your variables? 11:30 •Learning Outcome 2: Review 11:30 Keywords: Demonstrate your Learning for Outcome 2 •Neutralisation • Acid • Alkali Create • Antacid • Universal indicator • Variable Evaluate Apply (L5) •Did you: 1. Complete the experiment ? 2. Did you write a word equation for the reaction? 11:30 Which task(s) will you Analyse (L6) Analyseto choose •Did you: complete? Try to target a 1. Plan an investigation? Apply level higher 2. Identify the independent, dependent and control than your variables. current level. Understand 3. Complete the script and rehearse the play on neutralisation? Remember Learning Outcome 2: Review Go back to your Learning Outcome grid and fill out the ‘How I did’ and the ‘Targets’ column. Learning Outcome How I did Targets I am working at level .....because ........................... ........................... I can move up to level…... by …………………… …………………… Learning Outcome 2: Level 6 11:30 New Information for Learning Outcome 3 Explore and Discover: • Applications of Neutralisation •Insect Stings • Visual: • Audio: • Kinaesthetic: Bee stings are acidic and can be neutralised with baking soda (bicarbonate of soda). Wasp stings are alkaline and can be neutralised with vinegar. • Indigestion: Our stomach carries around hydrochloric acid. Too much of this leads to indigestion. To cure indigestion, you can neutralise the excess acid with baking soda or specialised indigestion tablets. 11:30 Useful acid-alkali reactions Food preservation – pickling involves soaking the food in vinegar which kills the bacteria which causes food to decay Hair and skin care – the best pH for skin is 5.5. Soaps containing very weak acids or alkalis can be used to get this pH level Stings – BEE stings are ACIDIC and are treated using an alkali such as calamine lotion which neutralises the acid of the sting. WASP stings are ALKALINE and are neutralised using an acid such as vinegar Soil treatment – acid rain can turn soil acidic. Some plants will not grow in acidic soil. The soil is neutralised using LIME which is an alkali Learning Activities for Outcome 3 • • • • • Questions Acid rain can be reduced by: 1) (a) What is "acid rain"? (b) Describe, in detail, how "acid rain" is formed. 2) Describe some of the problems caused by "acid rain". • 3) Describe 3 ways of reducing "acid rain" and explain how each way does so. 11:30 Demonstrate your Learning for Outcome 3 Evaluate (L7) Judge Justify Defend Decide Agree Value Prove Check Criticise Recommend Support Test Keywords: Acid rain, Fuel Neutralisation Create Nitrogen dioxide Evaluate Which task(s) will you choose to Analyse complete? Try to target a level higher thanApply your current level. Understand 11:30 Sulphur dioxide Remember Catalytic converter scrubbers Analyse (L6) Have you plan your investigation and identified the variables? Learning Outcome 3: Review Go back to your Learning Outcome grid and fill out the ‘How I did’ and the ‘Targets’ column. Learning Outcomes How I did Targets I am working at level .....because ........................... ........................... I can move up to level…... by …………………… …………………… Learning Outcome 3: Level 7 11:30 Review • Compare acids and alkalis. • Name the type of reaction that occurs when an acid and an alkali are added together. • Predict the products of adding hydrochloric acid to sodium hydroxide. 11:30 Quiz busters • Boys Vs Girls • Only use each player once. • Try to complete a line in your colour across or down the board. Review • Swap books with the person next to you and look over their work. Write a WWW and EBI statement. • Stand up if you have developed some skills this lesson? What are they? • Tell the person next to you three things you have learnt this lesson. • Did you successfully complete tasks at your target level? • If not, what do you need to do next in order to meet your target level? Record this in your diary to be done as part of your extended learning at home. • Is there any part of the lesson you think you need to go over again next lesson? • How will you remember what you have learned today for your exam? 11:30 •Technician list •A range of antacids •Universal indicator •three test tubes, •distilled water, •glass beaker, •dilute acid, •safety glasses. •very hot water, •100cm³ measuring cylinder •Sodium bicarbonate