Lesson Objective Outcomes/skills
advertisement
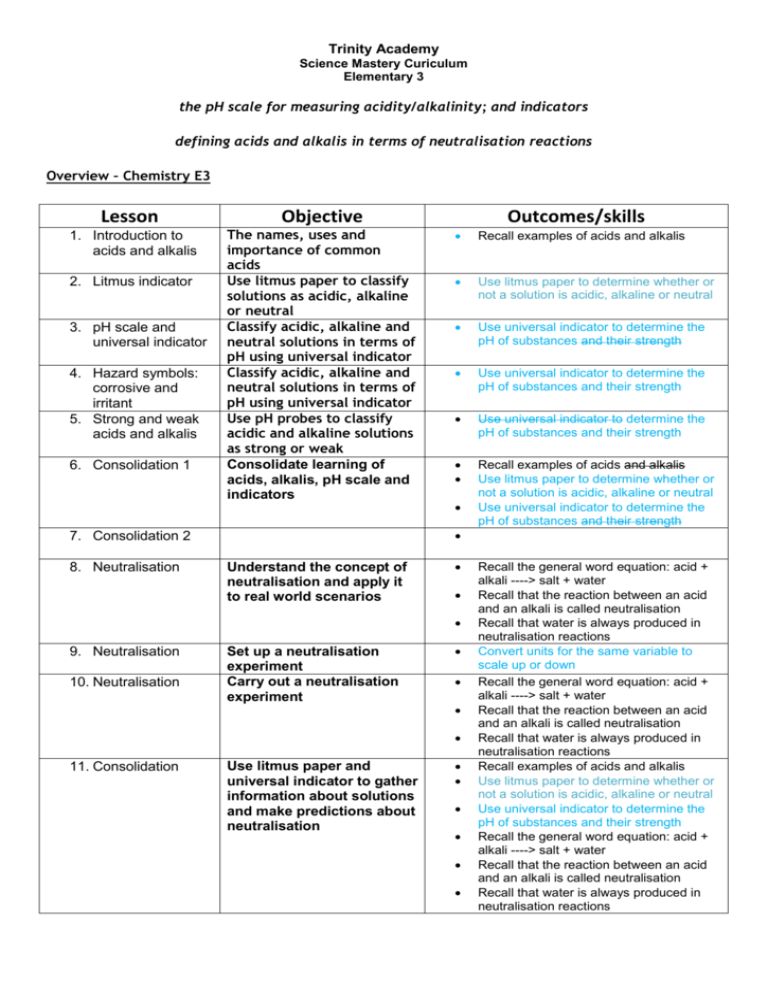
Trinity Academy Science Mastery Curiculum Elementary 3 the pH scale for measuring acidity/alkalinity; and indicators defining acids and alkalis in terms of neutralisation reactions Overview – Chemistry E3 Lesson Objective 1. Introduction to acids and alkalis The names, uses and importance of common acids Use litmus paper to classify solutions as acidic, alkaline or neutral Classify acidic, alkaline and neutral solutions in terms of pH using universal indicator Classify acidic, alkaline and neutral solutions in terms of pH using universal indicator Use pH probes to classify acidic and alkaline solutions as strong or weak Consolidate learning of acids, alkalis, pH scale and indicators 2. Litmus indicator 3. pH scale and universal indicator 4. Hazard symbols: corrosive and irritant 5. Strong and weak acids and alkalis 6. Consolidation 1 Recall examples of acids and alkalis Use litmus paper to determine whether or not a solution is acidic, alkaline or neutral Use universal indicator to determine the pH of substances and their strength Use universal indicator to determine the pH of substances and their strength Use universal indicator to determine the pH of substances and their strength Recall examples of acids and alkalis Use litmus paper to determine whether or not a solution is acidic, alkaline or neutral Use universal indicator to determine the pH of substances and their strength 7. Consolidation 2 8. Neutralisation Outcomes/skills Understand the concept of neutralisation and apply it to real world scenarios 9. Neutralisation 10. Neutralisation Set up a neutralisation experiment Carry out a neutralisation experiment 11. Consolidation Use litmus paper and universal indicator to gather information about solutions and make predictions about neutralisation Recall the general word equation: acid + alkali ----> salt + water Recall that the reaction between an acid and an alkali is called neutralisation Recall that water is always produced in neutralisation reactions Convert units for the same variable to scale up or down Recall the general word equation: acid + alkali ----> salt + water Recall that the reaction between an acid and an alkali is called neutralisation Recall that water is always produced in neutralisation reactions Recall examples of acids and alkalis Use litmus paper to determine whether or not a solution is acidic, alkaline or neutral Use universal indicator to determine the pH of substances and their strength Recall the general word equation: acid + alkali ----> salt + water Recall that the reaction between an acid and an alkali is called neutralisation Recall that water is always produced in neutralisation reactions