Acids and alkalis File
advertisement

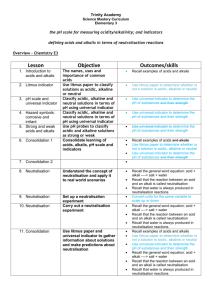
13/04/2015 Chemistry My family and home 13/04/2015 Acids and bases (alkalis) Used by the body, used in other processes: such as food, farming and chemical industries. Chemistry Lesson • • • • • Safety in chemistry Acids and alkalis (bases) Neutralisation Using indicators Practical work 13/04/2015 Hazard signs to learn… flammable Corrosive h i Harmful Irritant 13/04/2015 Hazard signs to learn… Radioactive Oxidising Toxic Dangerous for environment 13/04/2015 Safety • Irritant- can cause a rash or itching • Harmful-general damage to living organisms • Corrosive-will burn through materials 13/04/2015 Safety instructions • Wear goggles • Follow safety instructions 13/04/2015 Acids and bases 13/04/2015 • Acid- A substance that produces hydrogen ions (H+) when it dissolves in water. • Bases- Compounds which react with acids to neutralise them • Alkali- A soluble base, forms hydroxide OH- ions in water. • Neutral-not an acid or base Symbols in word equations -states of matter • • • • (l) liquid (g) gas (s) solid (aq) aqueous-dissolved in water 13/04/2015 Acids and bases (alkalis) 13/04/2015 Acid 13/04/2015 • Examples of acids include : • Vinegar, orange or lemon juice, acid rain, stomach acid, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acids • Used in car batteries, food and drinks, preserving food, in body. Acid • Hydrochloric acid is formed when hydrogen chloride is gas dissolves in water. • HCl (g) H+ (aq) + Cl-(aq) 13/04/2015 Alkali (bases) • Examples and uses include: metal hydroxides, metal oxides, cleaning products, stomach antacids, baking powder. 13/04/2015 Alkali • Sodium hydroxide is formed when the solid is dissolved in water. • NaOH (s) Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq) 13/04/2015 What is an acid? Is an alkali (OH or H) Give a use of an acid 13/04/2015 pH scale 1. An Indicator is a dye that changes colour 2. Indicators can be used to find out whether a solution is acid, alkaline or neutral 3. Universal Indicator can be used to find the pH of a solution • Acid – red, pH less than 7 • Neutral – green, pH = 7 • Alkali – blue, pH greater than 7 Universal Indicator and the pH scale 13/04/2015 Universal Indicator is a mixture of liquids that will produce a range of colours to show how strong the acid or alkali is: 0-14 0 1 2 3 Stomach acid 4 5 Lemon juice 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Water Soap Baking powder Oven cleaner Strong acid Strong alkali Neutral pH scale pH scale pH scale Practical 1 • Test chemicals to find pH • Use paper and liquid • Record results in a table 13/04/2015 Neutralisation 1. Acids react with alkaline solutions to form a salt and water • Hydrochloric acid produces chlorides • Nitric acid produces nitrates • Sulphuric acid produces sulphates 2. Ammonia can dissolve in water to produce an alkaline solution. This can be neutralised with acids to produce ammonium salts 3. Indicators can monitor neutralisation reactions Neutralisation 13/04/2015 An acid and alkali will neutralise each other (if the correct amounts are used): Acid + alkali Salt + water Acid + base Salt + water E.g. hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide sodium chloride + water Neutralisation • • • • • • Acids and bases neutralise each other. Acids form H+ (aq) ions in water Alkalis form OH- (aq) ions in water Acid + alkali salt + water H+ + OH- H2O The other parts form the salt. 13/04/2015 Neutralisation – Hydrochloric acid Neutralisation – Sulphuric acid Neutralisation – Nitric acid Questions 13/04/2015 • Write a word equation for adding hydrochloric acid to magnesium hydroxide • Extension : Write a balanced symbol equation for this reaction (difficult) Hint • Mg(OH)2 • MgCl2 Answers 13/04/2015 • Acid + base salt + water • Hydrochloric acid + Magnesium hydroxide magnesium chloride and water • 2HCl + Mg(OH)2MgCl2+2H2O Neutralisation – Fertiliser Practical 2 • Titrations and neutralisation 13/04/2015 Useful acid-alkali reactions 13/04/2015 1) Hydrochloric acid is used in the stomach to help _______. If we eat too many “rich” foods our stomachs create too much ____ – this is called ______. This acid needs to be neutralised by taking indigestion tablets. 2) Soil is naturally acidic, mainly due to acid ____. This can have bad effects on ____ and vegetable growth, so the excess acid may need to be neutralised with an _____ . Words – plant, digestion, indigestion, alkali, rain, acid Quiz on acids and alkalis Acid, alkali or both??? 1) This a pH of less than 7 2) This would turn Universal indicator green 3) This is often used in cleaners or soap 4) This would turn Universal Indicator red 5) Sodium hydroxide is a common ____________ 6) This would feel soapy on your skin 7) This could be a corrosive 8) This will turn universal indicator purple 9) This would taste sour 10) Lemon juice and vinegar are examples of weak _____ 13/04/2015 Acids and metals • Acid + metal Salt + hydrogen 13/04/2015 Metals and acids 13/04/2015 • The more reactive the metal, the faster the reaction • The speed of reaction is indicated by the rate at which bubbles of hydrogen are produced. • Test for hydrogen???? • Name of salt depends on metal and acid used Reaction of Metals and Acid Hydrochloric acid 13/04/2015 • Produces Chloride salts • Magnesium + Hydrochloric acid Magnesium Chloride + ________ • _______ + Aluminium +Aluminium Chloride + __________ • ________+ ________ Zinc chloride + _________ Hydrochloric acid 13/04/2015 • Produces Chloride salts • Magnesium + Hydrochloric acid Magnesium Chloride + hydrogen • Hydrochloric acid + Aluminium +Aluminium Chloride + hydrogen • Hydrochloric acid+ zinc Zinc chloride + hydrogen Symbol equations • 2HCl + Mg MgCl2 +H2 • ____HCl + 2Al 2AlCl3 + 3H2 • 2____ + ____ZnCl2 + H2 13/04/2015 Symbol equations • 2HCl + Mg MgCl2 +H2 • 2HCl + 2Al 2AlCl3 + 3H2 • 2HCl + ZnZnCl2 + H2 13/04/2015 Sulfuric acid reactions 13/04/2015 • H2SO4 + ______ MgSO4 + H2 • 3H2SO4 + 2Al Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2 • H2SO4 +Zn ZnSO4 + H2 • Copy and complete write a word equation for each. Sulfuric acid reactions 13/04/2015 • H2SO4 + Mg MgSO4 + H2 • 3H2SO4 + 2Al Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2 • H2SO4 +Zn ZnSO4 + H2 • Sulfuric acid + magnesium Magnesium sulfate + hydrogen Nitric acid • Nitric acid reacts with alkalis, but when reacting with metals it can produce nitrogen oxides. 13/04/2015 Metal Oxides & Hydroxides 1. Transition metal oxides and hydroxides do not dissolve in water. They are called bases 2. They react with acids to produce salts that are soluble 3. The excess metal oxide can be filtered off Metal hydroxide • Metal hydroxide + acid salt + water 13/04/2015 Metal oxide • Metal oxide + acid salt + water 13/04/2015 Adding acid to carbonates 13/04/2015 Carbonates are compounds containing carbon and oxygen. When an acid is added to a carbonate the carbonate starts to fizz. A gas called _________ _______ is produced. Calcium carbonate + hydrochloric acid CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) calcium chloride + carbon dioxide + water CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) Metal carbonate 13/04/2015 • Metal carbonate + acid water + salt + carbon dioxide Quiz