Human Reproductive Systems
Male Reproductive System
• Testes: male gonads
– Form male gametes (sperm) in ________________________
• Scrotum: sac that holds testes outside of body cavity
– Sperm develop optimally ____________________________
____________________________________.
• Epididymus: _______________________ to mature
• Penis:
– fleshy tube with ____________
allowing to internal fertilization
• Vas Deferens:
– carries sperm ______________
____________ during ejaculation
• Semen:
– transport medium for sperm
– Made up nutrient fluid to
nourish and protect sperm in
female reproductive tract
• Urethra:
– tube where semen exits penis
– Shares same structure with
_____________________
• Vasectomy:
– _______________________,
preventing sperm from leaving
the body
• Testosterone:
– produced by _____________
– plays a role in development of
male secondary sex
characteristics
• FSH and LH:
– secreted by ______________
– help in growth and
development of sperm in testes
Female Reproductive System
• Ovaries: female gonads
– Produce eggs
– Secrete _______________
– Each contains about 200,000
tiny egg sacs called __________
– One egg is released each month
during ____________________
– Estrogen:
• causes development of female
secondary sexual characteristics
• Breast development, broadened
pelvis, distribution of body fat
• Fallopian Tubes or Oviducts:
– near each ovary but not directly
connected to it
– ____________line tube and create
current that draws the released egg
towards uterus
– Where egg is __________________
• Uterus:
– thick walled muscular organ where a
fertilized egg will implant and grow
• Cervix:
– narrow _____________________
• Vagina:
– ____________________, site where
sperm is deposited
• Note: Urinary and reproductive tracts
are separate in females
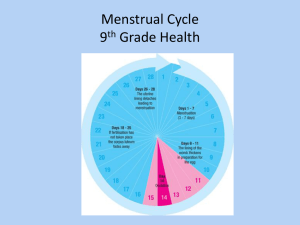
Menstrual Cycle
Series of hormonally controlled
changes that occur to the ovary and
uterine lining
• Basic Steps of Cycle:
– Egg matures and erupts from its follicle entering fallopian tube.
– Wall of the uterus has __________________ with a rich supply of blood
vessels (endometrial lining) and is prepared to receive a fertilized egg
– If egg not fertilized, lining breaks down and passes from the body as
menstrual fluid and cycle begins again
Stages of Menstrual Cycle
• Controlled by _____________________________
– Brain (FSH & LH) and ovary (estrogen & progesterone)
• Follicle Stage (10-14 days)
– _____________________ follicle
stimulating hormone (FSH)
causing follicle in ovary to mature
– ____________ gets secreted by
follicle in ovary as it develops,
causing uterine lining to thicken
• Ovulation (middle of cycle)
– Increased estrogen causes
pituitary to lower FSH and begin
secreting _______________ (LH)
– When this reaches certain level
ovulation occurs and __________
________________ releasing egg
– Egg must be fertilized in about 24
hours or it dies
• Corpus Luteum Stage (10-14 days)
– Ruptured follicle forms corpus luteum (yellow body) which
secretes ______________________
– Progesterone maintains the _________________________
• Menstruation (3-5 days)
– If fertilization doesn’t happen, LH secretion decreases,
corpus luteum breaks down and ________________drops
– Uterine lining is no longer maintained and ______________
and is released as ____________________
Menopause: the permanent
cessation of the menstrual cycle
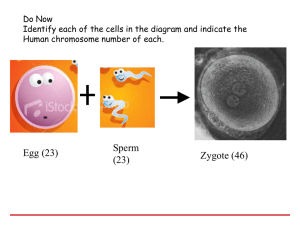
Human Fertilization & Development
• Fertilization: (Internal)
– ejaculation of _________________________ into vagina
– sperm swim through cervix into uterus and into Fallopian tube where
fertilization takes place
– one sperm breaks through membrane surrounding egg and fuses with
egg nucleus forming ___________________
• Gestation: the period of development ____________________
In Vitro Fertilization
Egg is fertilized with sperm _______________ then
placed into uterus several days later where it can implant
Embryo
Development
• In Fallopian Tube:
– fertilization occurs
– ____________ occurs
– ________ and ________ stage
http://www.dnatube.com/video/1127/Human-Reproduction-Fertilization-and-Fetal-Development
is reached
• In Uterus
– ______________ occurs
– embryo attaches itself to the
lining of uterus
– _______________ and
__________________occur
– Forms 3 layers from which
different tissues develop
• Ectopic Pregnancy
– Sometimes the embryo implants someplace other
than uterus (in oviduct or even in the abdomen).
This often results in the death of the embryo and
or the mother.
• Fraternal Twins:
– fertilization __________________
• Identical Twins:
Multiple
Embryos
– __________________ and splits into two separate embryos
– Conjoined Twins: when identical twins don’t separate
completely
Protecting & Nourishing Embryo
• Chorion:
– forms small fingerlike projections called
_______________ that extend into uterine
lining
• Placenta:
– uterine lining and chorionic villi come
together
– villi constantly bathed in ______________
– exchange of nutrients, oxygen and wastes
takes place here
• Umbilical Cord:
– rope like structure connects developing
fetus to placenta
• Amnion:
– membrane sack surrounding fetus
– filled with ___________________
– protects fetus from shock
• Amniocentesis:
– testing amniotic fluid for chromosomal and
developmental disorders
• Labor:
– uterine muscles _________
– opening to cervix gets larger
Labor & Birth
• Eventually amniotic sac
bursts open and baby
passes through birth canal
• Shortly after the ________
or “afterbirth” is expelled
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BgZ5z6RB06c&safe=active
• Nova: The Miracle of Life
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wou1Udu_vr8
&safe=active
• Nova: Life’s Greatest Miracle
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=swYuEkzTkV0
&safe=active
• Excellent for extra credit!!
• And both are related to your test!!