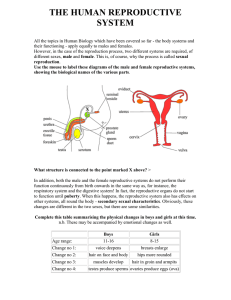
Female Reproduction System
advertisement

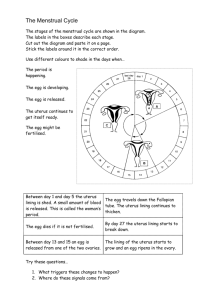
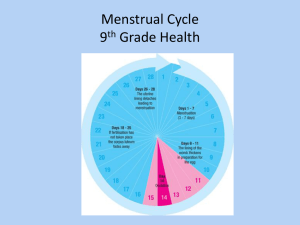
The purpose is to reproduce! To make a baby! (Same as the male reproduction system!) Tubular organ that: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Connects the outside of the body to the uterus Receives sperm during reproduction Allows menstrual flow to exit the body Passage of baby Produces fluids to cleanse and lubricate itself Provides sensation 1. Produces a mucous plug to keep germs out during pregnancy 2. Produces fluids to help sperm travel 3. Dilates 10 centimeters during childbirth to allow baby to pass Uterus: Muscular cavity size of fist and meets the vagina at the lower end of the cervix 1. Houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby 2. Allows nutrient and waste exchange with placenta; 3. Nourishes an embryo before a placenta grows 1. Transports egg from ovary to uterus Tiny finger-like structures at the end of the fallopian tube that pulls an egg from the ovary into the fallopian tube to be fertilized. Two are found deep in the pelvic area 1. Produce eggs 2. Produce estrogen and progesterone What does Estrogen and Progesterone do? * Cause growth of pubic and underarm hair * Strengthen bones * Regulate the monthly release of an egg * Prepare body for pregnancy What is it? 1. Monthly series of hormone controlled changes that prepare uterine lining for pregnancy 2. Release of an egg is called OVULATION 3. Uterine lining thickens to prepare for possible implantation of fertilized egg Ovulation takes place in the MIDDLE of the cycle, usually around day 14 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TExPlAh1tCA&feat ure=related 1. Estrogen and progesterone levels fall, and MENSTRUATION occurs 2. Menstruation: Breakdown and discharge of uterine lining out of the VAGINA 3. During this time, females use sanitary pads or tampons to absorb blood and tissue 4. Usually lasts between 3-7 days Perform after shower at least 1 week after menstrual period 1. Stand in front of mirror. Place one hand over head, and use the other to examine each breast. 2. Use thumb and index finger to squeeze nipple and look for unusual discharge 3. Check for swelling, dimpling, or scaliness 4. Use 3 to 4 fingers to feel each breast for unusual lumps or thickening under skin. Check under armpits and between breasts, too. Test to check for pre-cancerous cells in cervix The doctor will put a special instrument called a speculum into the vagina to open it so the sample can be taken. The doctor will collect a sample of cells ***Ask for a FULL STD test if you’ve been sexually active when you have a pap smear done!!!!***