cleavage - abcscience.net
advertisement
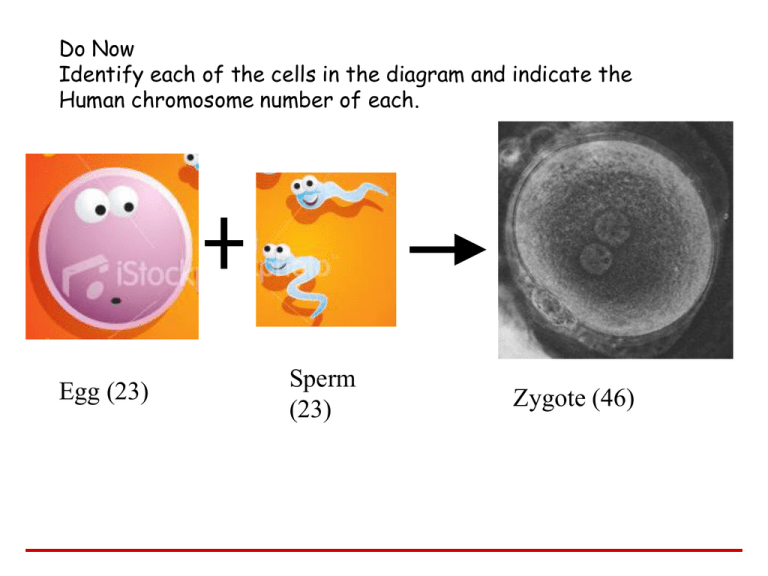
Do Now Identify each of the cells in the diagram and indicate the Human chromosome number of each. Egg (23) Sperm (23) Zygote (46) How do we go from a zygote (a single cell) to a multicellular organism? (hint: think about a process used to increase cell#) STAGES OF EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT • Series of steps leading from zygote to organism 1. Cleavage – increase in cell# by rapid mitosis, no cell growth 2. Differentiation – cells get their jobs by “reading” different parts of DNA, form tissues and organs 3. Growth Stage 1 • Egg and sperm are produced by MEIOSIS (gametogenesis). • They contain half as much genetic material as parent cells (in humans = 23) • The joining of the two nuclei is called fertilization • This can occur internally or externally Stage 2 1 The sperm approaches the egg SPERM 2 The sperm’s enzymes digest the egg’s jelly coat 3 The plasma membranes of sperm and egg fuse Sperm head 4 The sperm nucleus enters the egg cytoplasm Nucleus Egg nucleus EGG CELL 5 The nuclei of sperm and egg fuse 46 •Normal fertilization: http://www.stanford. edu/group/Urchin/nf ert.htm Sperm nucleus Jelly coat • The fertilized egg or Zygote now has how many chromosomes? Zygote nucleus 2-cell stage Stage 3 • The fertilized egg divides into two new cells by MITOSIS to form identical cells • This is the beginning of cleavage: rapid increase in cell #’s by mitosis (stages 3-4) • NO CELL GROWTH! • # of chromosomes in each cell: 46 http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/150/devel/blastula.gif Stage 4 • Four Cell Stage: still increasing in numbers by mitosis (cleavage) • Number of chromosomes in each cell: 46 Stage 5 • Blastula: hollow ball stage • Number of chromosomes in each cell: 46 • The layer of cells is generally one cell thick and the cavity is filled with fluid • Cell growth starts Stage 6 • Gastrulation: inward pushing of blastula to form two layers (indentation) • The cell is beginning to grow before dividing Stage 7 • Differentiation: formation of three layers which will develop into organs and organ systems • Development can take place internally or externally Twins • Fraternal Twins – two separate eggs fertilized by two separate sperm (dizygotic) •Identical Twins – single egg is fertilized , zygote splits early (monzygotic), have identical DNA • Indian girl - born fused at the pelvis to a "parasitic twin" that stopped developing in the womb • She had absorbed the organs and body parts of the other fetus, a condition that occurs once in 50,000 conjoined twin births. Fertilization and Cleavage Video Clip • http://trc.ucdavis.edu/biosci10v/bis1 0v/media/ch27/cleavage_implant.ht ml • http://www.unc.edu/~fconlon/Danie lResearch.htm • http://raven.zoology.washington.edu /celldynamics/events/workshops/arc hive/2003/cytomod_abstracts/GvD_ VDF/images/GvD-VEF-fig1.jpg • http://www.howstuffwork s.com/adam-200048.htm Stem cells – cells without a “job”, removed from blastocyst before they differentiate