Reproduction LP
advertisement

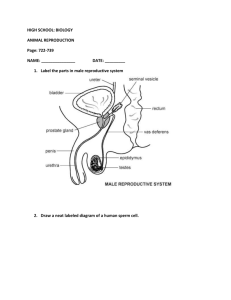
Topic: Biological Animal Science Unit: Animal Reproduction Frameworks: 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4 Objectives: 1. Define terms related to animal reproduction in class notes with 100% accuracy. 2. Identify the parts of the male and female reproductive systems and the functions of each with 90% accuracy. 3. Discuss the sexual reproduction processes of agricultural animals in class notes with 100% accuracy. Lesson: Terms: o Copulation o Corpus luteum o Embryo transfer o Estrogen o Estrous cycle o Estrus o Follicle o Follicle stimulating hormone o Gestation o Hormone o Hybridization o Inbreeding o Ovulation o Oxytocin o Parturition o Progesterone o Selective breeding o Super ovulation o Testosterone o Zygote Sexual reproduction- begins with copulation (mating of male and female) o Fertilization occurs when the sperm penetrates the egg. o Embryo- fertilized egg; new animal o Embryo transfer- moving an embryo from one female animal to another of the same species Male reproductive system o Testicles produce sperm (male sex cell) and testosterone (causes the appearance and behavior of the animal to be masculine o Epididymis- Storage site for sperm cells From the testicles, sperm cells enter the epididymis to mature Separate epididymis is attached to each testicle o Scrotum Sac that contains and protects the two testicles Also regulates the temperature of the testicles which is lower than the body temperature of the animal Maintaining the correct temperature is critical because extreme temperatures can affect the production and vitality of sperm o Vas deferens Transportation tube that carries the sperm-containing fluid from each epididymis to the urethra o Urethra Large, muscular canal extending from the urinary bladder Both semen and urine move through the urethra to the end of the penis o Accessory sex glands Several glands that add volume and nutrition to the sperm-rich fluid coming from the epididymis Seminal vesicles Open into the urethra Produce a fluid that protects and transports the sperm Prostate gland Produces a fluid that is mixed with the seminal fluid Cowper’s gland Produces a fluid that moves down the urethra ahead of the seminal fluid o Cleans and neutralizes the urethra which helps protect the sperm as they move through the urethra o Mixture of the seminal and prostate fluid and the sperm is called semen. o Penis Deposits the semen within the female reproductive system Female reproductive system o Ovary Produces female gametes (sex cells)- ova (eggs) Follicle- a small blister-like development on the surface of the ovary that contains the developing ovum Follicle stimulating hormone- a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that promotes growth of ovarian follicles in the female and sperm in the male o Oviducts Two tubes that carry the ova from the ovaries to the uterus Also called fallopian tubes At ovulation, the follicle ruptures, releasing an ovum that is caught by the infundibulum. After copulation, sperm move through the uterus to the oviduct. Fertilization occurs in the upper end of the oviduct. The zygote (fertilized egg) moves to the uterus 2-4 days after fertilization o Uterus A Y-shaped structure consisting of the body, two uterine horns, and the cervix, size and shape of the uterus varies among mammals Upper part of the uterus consists of the uterine horns that develop into the oviducts Mammals that normally produce large numbers of offspring at each breeding have large horns and small body Fetus grows within the uterus where it remains until parturition (birth) Cervix- lower outlet of the uterus and constitutes the gateway between the uterus and the vagina o Vagina Female organ of copulation Birth canal Passage between the cervix and vulva Lining is moist during estrus and dry when the animal is not in estrus o Vulva External opening of the reproductive and urinary systems o Clitoris Sensory and erectile organ of the female Located just inside the vulva Reproductive systems of poultry o Male Testicles Held inside the body cavity Produce sperm and seminal fluid Vas deferens Carries the seminal fluid and sperm cells to the cloaca Cloaca Enlarged part where the large intestine joins the end of the alimentary canal Alimentary canal Food-carrying passage that begins at the mouth and ends at the vent Papilla Organ in the wall of the cloaca that puts the sperm cells into the hen’s reproductive tract o Female Ovaries and oviducts- The right ovary and oviduct do not function Only left ovary and oviduct produce eggs The ova produced in the ovary develop into egg yolks Oviduct has 5 parts: o Funnel- recieves the yolk from the ovary; sperm cells are stored here o Magnum- secretes the thick white of the egg o Isthmus- two shell membranes are placed around the yolk and thick white o Uterus- thin white and outer shell are added to egg; egg remains here for approximately 20 hours o Vagina- egg stays here until it is laid It takes approximately 25-27 hours for a chicken to produce one egg. Estrous cycle o the time between periods of estrus o Estrus- heat; time during which the female will accept the male for copulation o Begins when a follicle on the ovary begins to develop o Estrogen (a hormone produced by the ovaries) is produced and causes the animal to show signs of estrus o Super ovulation- the stimulation of more than the usual number of ovulations during a single estrous cycle due to the injection of certain hormones Ovulation o Release of the egg cell from the ovary o Time of ovulation is usually near the end of the estrous period o Egg cell is contained in the follicle; follicle breaks open, releasing the egg; egg moves into one of the oviducts o Shortly after ovulation, the corpus luteum (a reddish-yellow mass that forms in a ruptured follicle in the ovary of mammals) from on the ovary Hormone progesterone is released A hormone that maintains pregnancy in the animal Gestation- length of pregnancy o Fetus develops in the uterus o Umbilical cord connects from the navel of the fetus to the placenta Supplies nutrients and oxygen and carries off waste products o Fetus grows slowly Most growth occurs in last trimester of gestation period Parturition- act of giving birth o Near the end of gestation period, the corpus luteum reduces the production of progesterone o Increase in amount of estrogen in body Causes the uterine muscles to contract Begins process of birth o Oxytocin- a hormone that causes contractions of the uterus during breeding and parturition and causes milk letdown Selective breeding- the breeding of selected animals chosen because of certain desirable qualities or fitness o Hybridization- the production of hybrids by natural crossing or by manipulating crossing o Inbreeding- the mating of closely related animals Review: Parts of reproductive systems worksheet Source: MyCaert.com—Animal Reproduction