File
advertisement

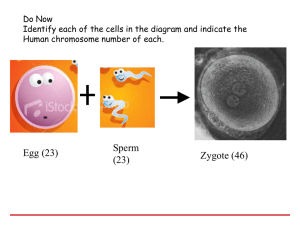
Name: _______________________________Date: Class: The Reproductive System CRCT Coach Book: Pages 77-79 Two types of reproduction: • • Sexual: two parents; offspring is a mixture of DNA from both parents Asexual: one parent; offspring is genetically identical to the parent example: bacteria, some protists, fungi, some plants & animals Benefits • • • Sexual reproduction leads to genetic variation within a population without which there could be no evolution Asexual: 1. lots of offspring quickly 2. don’t need to find a mate Human life begins with the joining of two specialized cells gametes from two parents. Male gamete: sperm Female gamete: egg When the egg and sperm join it is called fertilization • The fertilized egg is called a zygote. • • • Chromosome Count • • Human body cells have 46 chromosomes that form 23 pairs. Gametes are produced through a process called meiosis which reduces the chromosome number by ½ to 23 • All offspring produced through sexual reproduction get half of their chromosomes from each parent Male Reproductive System • The main job of the male reproductive system is to produce sperm and deliver it to a woman’s fallopian tube so it can fertilize the egg. • • • • The main reproductive organs in males are the testes (singular testis), or testicles. The testes are located outside the body in a sac called the scrotum. Structures include testes, scrotum & penis. The sperm exit the male body through the penis. Hormones • • • • Sperm development results from the release of hormones. A hormone is a chemical made in one part of the body that affects the activities of cells in other parts of the body. The blood carries hormones through the body. Once males begin to produce sperm, they can do so for the rest of their lives. Female Reproductive System Functions: to produce eggs that carry the female’s genetic information and, if an egg is fertilized, to nourish a developing baby until birth. Organs include ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus & vagina. • • • There are two - one on each side Comes from the Latin word ova, meaning “eggs” Females are born with all the eggs they will ever have. Path of the Egg • • • • • • • Each ovary is connected to a fallopian tube The fallopian tubes transport eggs (usually one egg each month) from the ovaries to the uterus. While it is in the fallopian tube, the egg may be fertilized by sperm from a male. The uterus is an organ with strong, thick muscular walls that holds and nourishes a growing embryo. If an egg is fertilized, it develops within the uterus. The baby exits the mother’s body through the vagina, or birth canal. The strong contractions that push the baby out of the mother’s body are called labor. Embryos Develop within a Placenta • • • Offspring cannot be produced unless an egg is fertilized by a sperm. The new cell formed when the sex cells unite is called a zygote. All multicellular organisms begin life as zygotes. Cell Division • Shortly after forming, the zygote undergoes a series of cell divisions. • Each cell division increases the number of cells in the zygote, so the embryo grows. • The early embryo is a ball of cells. Mammals and Birth • Human embryos, like those of most other mammals, develop within a placenta. • The placenta is a fluid-filled organ through which materials are exchanged between the mother and the developing offspring. • The embryo is connected to the placenta by the umbilical cord. • Pregnancy is the period from fertilization to birth. In humans, pregnancy lasts about nine months.