NounAdjectivePronounPowerpoint-2 - Miss Williams
advertisement

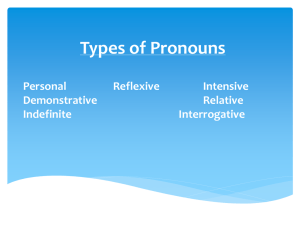
Reminders of some types of NOUNS A Quick Review A concrete noun: • Names a person, place, or thing that you can perceive using one of your senses. Concrete nouns: Students Desks Wall Restaurant Abstract noun: • Names an idea, feeling, a quality, or characteristic. • Abstract nouns: Danger Justice Love Collective noun • Collective nouns name a group A flock Crew A herd A troop Compound nouns • Made up of two or more words. Toothpaste Bedroom Blackboard Moving on to pronouns: • Types of pronouns Personal Pronouns Reflexive/Intensive pronouns Demonstrative and Relative pronouns Indefinite and Interrogative Personal pronouns • Personal Pronouns refer to certain specific persons, places or things. They change their form depending on person, number or gender. • Examples: I, he, they, them, you, it, ours, their, yours. Practice. Write the sentence. Circle the personal pronoun. 1. Where did they come from? 2. It was a long time ago, in the nineteenth century. 3. Mom told me that grandfather is from Sweden. 4. He brought two cousins with him. 5. She didn’t want to come at first. Practice. Write the sentence. Circle the personal pronoun. 1. Where did they come from? 2. It was a long time ago, in the nineteenth century. 3. Mom told me that grandfather is from Sweden. 4. He brought two cousins with him. 5. She didn’t want to come at first. Reflexive Pronouns • End with –self or –selves. They refer back to a noun or pronoun in a sentence. Examples: Myself Himself Itself Ourselves Jake imagined himself at the wheel of the car. Intensive Pronoun • Also end in –self or –selves but is used with a noun or another pronoun to emphasize the noun or pronoun. • Example: Henry Ford himself once drove the car. Write the sentence. Underline the reflexive or intensive pronoun. Label it “R” or “I”. • I gave myself plenty of time to get to work. • You should let yourself into the house. • The actress herself wrote those lines. • The cat itself caught the mouse. Write the sentence. Underline the reflexive or intensive pronoun. Label it “R” or “I”. • I gave myself plenty of time to get to work. R • You should let yourself into the house. R • The actress herself wrote those lines. I • The cat itself caught the mouse. I Demonstrative and Relative • Demonstrative points out a person, place, thing, or idea. Ex: That was Thomas Edison. Is This the very first light bulb? Relative: Introduces a subordinate clause. The car which I drove is old. My brother, whose phone you heard, is a doctor. Write the sentences. Underline the demonstrative or relative pronoun. Label it “D” or “R” • The chef who won the competition studied in Paris. • This tastes good. • I can’t stand dogs that bark loudly. • These shoes fit comfortably. Write the sentences. Underline the demonstrative or relative pronoun. Label it “D” or “R” • The chef who won the competition studied in Paris. R • This tastes good. D • I can’t stand dogs that bark loudly. R • These shoes fit comfortably. D Indefinite and Interrogative • Interrogative introduces a question. • Example: Who, What, Which • Indefinite refers to a person, place, a thing, or idea that is may or may not be named specifically. • Example: Anybody, both, few, neither, nothing, no one, everyone, several. Write the sentence. Underline the Indefinite or interrogative pronoun. Label it “I” or “inter” • • • • 1. Many rode bicycles for transportation. 2. Which is the most famous invention? 3. What was the name of the song? 4. Several rode to the event. Write the sentence. Underline the Indefinite or interrogative pronoun. Label it “I” or “inter” • 1. Many rode bicycles for transportation. I • 2. Which is the most famous inventions? INTER • 3. What was the name of the song? INTER • 4. Several rode to the event. I What is an antecedent? • An antecedent is a noun to which the pronoun refers. It usually goes before the pronoun ("ante" means before). • Examples: • Even though the party was fun, it was crowded. • People often like parties because they get to see old friends. Adjectives • Describes a noun or pronoun. Articles are considered adjectives. The articles are an, a, the. Examples: 1. The area, remote and primitive, is peaceful. 2. The small lions ate quickly. Check your practice. • The little town is in a quiet valley surrounded by tall mountains. • Some days the mountains look blue or purple. • A lazy river flows through the western part of town. • The water, deep and serene, looks beautiful with golden spots of sunlight on it. Demonstrative Adjectives They are used to describe a noun. This, that, these and those. (yes these are the same words you wrote for demonstrative pronouns BUT now they describe a noun). Examples: Demonstrative pronoun: This is the Australian outback. Demonstrative adjective: This land is the Australian outback. Check your practice. • Directions: Underline the demonstrative adjective (s) in each sentence. • These international students at the table with us put on the fair. • It is held in that brick building. • I bought this ring on my finger from a Greek student. • Those dolls in the next room are dressed in national costumes. • Karen made that African doll in the far corner. Proper Adjectives • When an adjective is formed from a proper noun. • Examples: Proper Noun Proper Adjective America an American city Palm Beach a Palm Beach vacation New York a New York newspaper Check your answers • This store is my favorite. ADJ • Both have wooden buttons. PRONOUN • These are the most popular albums. PRONOUN • Which test was the hardest for you? ADJ • This is a test for Ms. Alonso’s students. PRONOUN