Nouns
advertisement

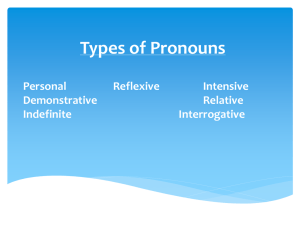
Language Arts Grammar - Nouns Nouns A noun is a word used to name a person, a place, a thing, or an idea. View the following examples: PERSONS PLACES THINGS IDEAS Alice Walker Desert Money Courage Dr. Lacy neighborhood Wind Love children outer space animals freedom architect New York City Voyager 2 luck team Grand Canyon equality Baby sitter Nigeria Statue of Liberty Newbery Medal gymnast Golden Gate orange juice democracy Self-control Compound Nouns A compound noun is two or more words used together as a single noun. The parts of a compound noun may be written as one word, as separate words, or as a hyphenated word. View the following examples: ONE WORD Seafood, filmmaker, videocassette, footsteps, grasshopper, Iceland, daydream, Passover SEPARATE WORDS compact disc, House of Representatives, police officer, John F. Kennedy, The Call of the Wild HYPHENATED WORD Self-esteem, fund-raiser, sister-in-law, fourteen-yearold, grand-parents Collective Nouns A collective noun is a word that names a group. View the following examples: Collective Nouns faculty, family, herd, team, congress, audience, flock, crew, jury, committee Common Nouns and Proper Nouns A common noun is a general name for a person, place, thing, or idea. A proper noun names a particular person, place, thing, or idea. Note: Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns begin with a capital letter only when they come at the beginning of a sentence. Common Nouns poem nation athlete ship newspaper river street day city organization language holiday Proper Nouns “The Raven,” “Casey at Bat” Canada, United States of America Ken Griffey Jr., Peyton Manning Mayflower, U.S.S. Constitution The New York Times, USA Today Ohio River, Kentucky River Hawkins St., Highland Ave. Friday, Independence Day Carrollton, Madison American Legion, Boy Scouts English, Spanish Thanksgiving, Labor Day Concrete Nouns and Abstract Nouns A concrete noun names a person, place, or thing that can be perceived by one or more of the senses (sight, hearing, taste, touch, or smell). An abstract noun names an idea, a feeling, a quality, or a characteristic. CONCRETE NOUNS Hummingbird, telephone, popcorn, ocean, Madison Milton Bridge, Jesse Jackson, sneeze, stone, refrigerator, rain ABSTRACT NOUNS Knowledge, love, humor, patriotism, beliefs, honor, beauty, peace, health, competition, Buddhism The Pronoun A Pronoun is a word used in place of one noun or more than one noun. Example: When Kelly saw the signal, Kelly pointed the signal out to John. When Kelly saw the signal, she pointed it out to John. The Pronoun Note: The word that a pronoun stands for is call its antecedent. Example: Mark read the book and returned it to the library. The photographers bought themselves new lenses. Personal Pronoun A personal pronoun refers to the one speaking (first person), the one spoken to (second person), or the one spoken about (third person). View the following examples: Personal Pronouns Singular Plural First Person I, me, my, mine we, us, our, ours Second Person you, your, yours you your, yours Third Person he, him, his, they, them, their, she, her, hers, it, theirs its Bell Ringer - Nouns • Without using your notes, give an example for each of the following nouns: • Noun = • Compound Noun = • Collective Noun = • Proper Noun = • Concrete Noun = • Abstract Noun = Reflexive and Intensive Pronouns A reflexive pronoun refers to the subject and directs the action of the verb back to the subject. An intensive pronoun emphasizes a noun or another pronoun. View the examples: Reflexive and Intensive Pronouns First Person myself, ourselves Second Person yourself, yourselves Third Person himself, herself, itself, themselves Reflexive and Intensive Pronouns Juan wrote himself a note as a reminder. (reflective) The rescuers did not consider themselves heroes. (reflective) Amelia designed the costumes herself. (intensive) I myself sold more than fifty tickets. (intensive) Demonstrative Pronouns A demonstrative pronoun points out a specific person, a place, a thing, or an idea. View the examples: Demonstrative Pronouns this that these those This is the most valuable baseball card I have. These are the names of those who volunteered. Interrogative Pronouns An interrogative pronoun introduces a question. View the following examples: Interrogative Pronouns what which who whom whose What is the largest planet in our solar system? Who scored the most points in the game? Relative Pronouns A relative pronoun introduces a subordinate clause. View the following examples: Relative Pronouns that what which who whom whose The Bactrian camel, which has two humps, is native to central Asia. Ray Charles is one of several blind performers who have had a number of hit recordings. Indefinite Pronouns An indefinite pronoun refers to a person, a place, or a thing that is not specifically named. View the examples: Indefinite Pronouns Everyone completed the test before the bell rang. Neither of the actors knew what costumes the other was planning to wear. Common Indefinite Pronouns all both few nobody several another each many none some any either more no one somebody anybody everybody most nothing someone anyone everyone one something anything everything neither other such much