Pronoun Reference
advertisement

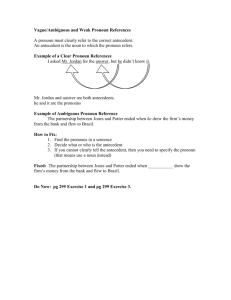
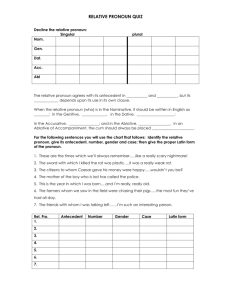
Make pronoun references clear. (A challenge for many ECA students.) What is a pronoun? • Pronouns substitute for nouns; they are a kind of short hand. In a sentence like After Andrew intercepted the ball, he kicked it as hard as he could, the pronouns he and it substitute for the nouns Andrew and ball. The word a pronoun refers to is called its antecedent. Differences between English & Spanish • In English, the pronoun is never dropped from the sentence because it is understood. You all know this, but some of you forget when you write and speak English. About Grammar Checkers • They do not flag problems with faulty pronoun reference. Grammar checkers would miss the ambiguous pronoun reference in the following sentence: The thief stole the woman’s purse and her car and then destroyed it. Examples of Ambiguous Reference • When Gloria set the pitcher on the glasstopped table, it broke. • BETTER—The pitcher broke when Gloria set it on the glass-topped table. Another Example • Tom told James that he had won the lottery. Who won the lottery—Tom or James? • BETTER—Tom told James, “You have won the lottery.” Implied Reference • A pronoun must refer to a specific antecedent, not to a word that is implied but not present in the sentence. FOR EXAMPLE • After braiding Ann’s hair, Sue decorated them with brightly colored ribbons. • BETTER—After braiding Anne’s hair, Sue decorated the braids with brightly colored ribbons. A Subtle Implied Reference • In Mary Gordon’s The Shadow Man, she writes about her father’s mysterious and startling past. • BETTER—In The Shadow Man, Mary Gordon writes about her father’s mysterious and startling past.