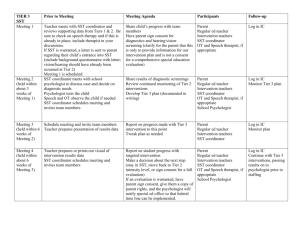
RTI
advertisement

Response to Intervention Kate Murray Shayna Stuempfig What is it? RTI is a data-driven, multi-tiered approach to the early identification and support of students with learning and behavioral needs. RTI is not a program but a process: a way to identify who is at risk and, more importantly, why. RTI helps us to support students within general education long before they fail, it can help us better identify those students with true disabilities in need of special education services, and it aims to avoid mislabeling students as disabled when they are not. Why do we need RTI? Our kids are continuing to fail despite amazing teachers and kick ass lessons There is an overrepresentation of African American students in special education (especially under Emotional Disturbance) Why are they failing? Lots of reasons! Stress, lack of sleep, lack of exercise, different learning styles, poor nutrition, poor vision, lack of opportunity to learn, chaos at home, processing issues, adolescent ridiculousness RTI is the process of learning why certain students are failing so we can help them be successful Many steps can be taken to help student succeed prior to referring them to special education It’s the Law Under RTI, schools will consider most students for special education services only after the students have not responded to a series of timely, systematic, increasingly focused and intensive research-based interventions, which are the responsibility of the regular education program. RTI is a part of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act (IDEIA) signed into law in 2004 What does RTI look like? Tier 3(5-10%) Intensive: Small Group/Individual Tier 2 (10-15%) Strategic: Small Groups/Lower class size or pre-teach class Tier 1 (80-90%) Benchmark/ Universal Access: All students What does this mean for you? If a student is continually struggling academically or behaviorally despite general classroom supports, you may call on a problem-solving team to help figure out the best way to support the student and how to best mobilize these supports/help/intervention. That problem solving team is our SST. Remember to invite all of the student’s teachers and notify Cyndi Baker-Smith by filling out one of the referral forms and putting it in her box. Put the date and time of the SST on the referral form. One of us will lead the SST SST meeting At the SST meeting teachers will set an academic or behavioral goal for the student and discuss possible interventions and supports. The teachers will leave with a student check-in packet that they will fill out over the following 6 weeks before the next SST meeting. This packet will help monitor the student’s response to the interventions put in place and be the data looked at when the SST meets again. This data will direct the team towards the best help for that student. Interventions vs. Supports INTERVENTIONS Something you do with a student to build a specific skill. Hot read/cold read, echo reading, pre-reading practice SUPPORTS Something you do to support a student who already has the skills or to motivate him or her to do other skillbuilding activities Student check-in, staying after school to finish work, seat change How to Intervene Tier 1 (80-90%): Universal Access Culturally and linguistically responsive instruction School-wide/classroom positive behavioral strategies High expectations and inclusive environment Researched-based differentiated instruction i.e. identifying students who are not learning skills in PLCs and planning small group work time to target skill building Progress monitoring Examples at Westlake After school program, parent resource center, schedule change, Kagan strategies, lunchtime/afterschool help How to Intervene Tier 2 (10-15%): Strategic SST process begins Small group, outside of core instructional time Before/afterschool for 30-60 minutes Referral to learning center to work with intervention teacher or specialist (i.e. Kate and Neku) Tier 1 continues plus more time, more focus, and more progress monitoring Examples at Westlake Math strategies, conflict management, girls’/boys’ group, modifications and accommodations in class How to Intervene Tier 3 (5-10%): Intensive Increased frequency and duration of skill building help More frequent progress monitoring Intensify SST process Examples at Westlake Read 180, individual counseling, one-on-one academic intervention, behavior contract, more frequent use of the learning center, referral to special education testing (last step) Special Education Referral We have 60 days to complete the assessment once the assessment plan is signed Expect students who are assessed to remain in your classroom Common disabilities include: Specific Learning Disability (SLD) Emotional Disturbance (ED) ADHD (OHI) Speech and Language Impairment (SLI) Questions??? Please contact us anytime throughout the year We are here to support you and use us as a resource