Using Response to Intervention
advertisement

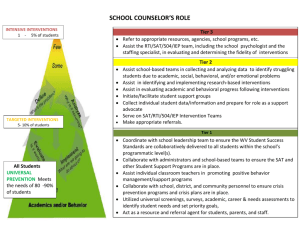
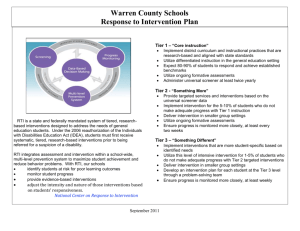
The ABC’s of PLC and RTI Shanna Brooks NCESD Literacy Specialist Resources: • Buffum, A., Mattos, M., & Weber, C. (2009). Pyramid Response to Intervention. Bloomington, IN: Solution Tree • Callender, Wayne (2009) Partners for Learning, Boise, ID • DuFour, R., DuFour, R., Eaker, R., & Many, T.(2006). Learning by Doing: A Handbook for professional learning communities at work. Bloomington, IN: Solution Tree • Mattos, M. (2009). Pyramid Response to Intervention: Part I Webinar. Solution-Tree.com • Using Response to Intervention (RTI) for Washington’s Students (2006), Dr. Terry Bergeson, OSPI A symbiotic relationship: a cooperative, mutually beneficial relationship between two people or groups Webster Professional Learning Community: • To Lead, Serve, and Support the Educational Community • A PLC is composed of collaborative teams whose members work interdependently to achieve common goals linked to the purpose of learning for all. DuFour - 2006 The Big Ideas of PLC: • Focus on Learning • Build a collaborative culture • Focus on Results Mattos - 2009 The PLC 4 Critical Questions: • What do we want all students to learn? • How will we know when they have learned it? • How will we respond when some students do not learn? • How will we respond when some students have learned? DuFour - 2006 For all students to learn, we must: • Start with a highly effective researchbased core instruction. • Systematically identify students who are not succeeding in our core program through valid assessments. • Provide additional time and support to struggling students with targeted interventions. Mattos - 2009 A Cultural Shift: • • • • • Ongoing Adult Learning Deliberate Teamwork “Our Kids” Data Driven Decisions Leverage Resources Response to Intervention: • IDEIA, 2004 • The reauthorization of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) in 2004 allowed RTI to be utilized as a component of an evaluation for special education eligibility. Response to Intervention: • Washington State RTI Manual • http://www.k12.wa.us/RTI/Resources/ RTIManual.aspx The Washington Model • • • • Use all school resources to help all students learn Use research-based programs and instructions Focus on the core program Universally screen students so that none fall through the cracks • Use a multi-tiered approach to meeting student needs • Use data decision-making • Monitor progress often Washington State Board of Education (2006) As cited in Pyramid Response to Intervention, Buffum (2009) Essential Characteristics of RTI: • Collective responsibility • Quality core instruction • Universal screening and diagnostic assessment • Research-based interventions • Progress monitoring • Quality problem solving • Certain access to appropriate instruction Mattos-2009 How well do we line up? • Use all school resources to help all students learn • Use research-based programs and instructions • Focus on the core program • Universally screen students so that none fall through the cracks • Use a multitiered approach to meeting student needs • Use data decision-making • Monitor progress often • Collective responsibility • Quality core instruction • Universal screening and diagnostic assessment • Research-based interventions • Progress monitoring • Quality problem solving • Certain access to appropriate instruction Three-Tier Model of School Supports: Tier 3 Intense Interventions Tier 2 Supplemental Interventions Tier 1 Core Instruction 5% of your students should be here. 15% of your students should be here. 80% of your students should be here. Tier 1 Benchmark: • • • • Designed for most Promotes 1 year growth in 1 year time Minimum time daily (i.e., 90 min) Ensures students across different classrooms receive same content Callender - 2009 Tier 2 Strategic: • • • • • 30-45 min. daily Small group In addition to the core Targets specific skill deficits Can be part of core or supplemental to core Callender - 2009 Tier 3 Intensive Intervention: • • • • • • Is comprehensive within content area Designed to accelerate if used properly 60 minute or more daily Smaller group Generally replaces the core May also need to be supplemented Callender - 2009 Assessments: • Universal Screening Tools – DIBELS, AIMSweb • Diagnostic Assessments – CORE, DAR, QRI, CBA’s • Progress Monitoring – DIBELS, NWEA MAPS, Read Naturally The A B C’s: • Access to quality teaching and learning for every student • Build a collaborative culture of professionals • Communicate & Celebrate Success