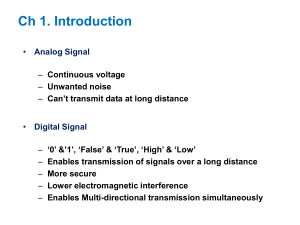
Digital IC Family
advertisement

Digital IC Family Digital IC Introduction • Digital ICs are more reliable by reducing the number of external interconnections from one device to another. • Before ICs, every circuit connection was from one discrete component to another. Cont., • A logic family refers to digital integrated circuit devices which are constructed with a combination of electronic gates. • A family has its own power supply voltage and distinct logic levels. Cont., • Each family has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages. • Also within each family, there is a range of voltages which may be high level or low level. Cont., • The various logic families can be placed into two brand categories according to the IC fabrication process. • Bipolar • Metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS) Bipolar Logic family Metal-oxide semiconductor Logic family Bipolar Logic families • The important elements of a bipolar IC are resistors, transistors and diodes. • Based on the two main operations of bipolar ICs, i.e., • Saturated • Non-saturated. Saturated bipolar Logic families • Resistor-Transistor Logic (RTL) • Direct-Coupled Transistor Logic (DCTL) • Diode-Transistor Logic (DTL) • High Threshold Logic (HTL) • Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL) • Integrated-Injection Logic (IIL) Resistor-Transistor Logic (RTL) Direct-Coupled Transistor Logic (DCTL) Diode-Transistor Logic (DTL) High Threshold Logic (HTL) Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL) Integrated-Injection Logic (IIL) Non saturated Logic families • Schottky TTL • Emitter-coupled Logic (ECL) Emitter-coupled Logic (ECL) Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) The MOS families include • PMOS p-channel MOSFETs • NMOS n-channel MOSFETs • CMOS Complementary MOSFETs PMOS p-channel MOSFETs NMOS n-channel MOSFETs CMOS Complementary MOSFETs Characteristics of Digital ICs • Speed of operation • Power dissipation • Fan-in • Fan-out Cont., • Noise immunity • Operating temperature • Power supply requirements Speed of operation • The speed of operation of an IC is expressed in terms of propagation delay. • Propagation delay is defined as the time taken for the output of a gate to change after the inputs have changed Cont., • The time difference between the application of input and appearance of output is also called as propagation delay. Power dissipation • Power dissipation is the nature of the power consumed by a logic gate when fully driven by all its inputs. • It is expressed in mill watts or nano watts Fan in • The fan-in of a gate is the number of inputs connected to the gate without degradation in the voltage levels. Fan out • Fan out is the maximum number of similar logic gates that a gate can drive without any degradation in voltage levels. Noise immunity • The noise immunity of a logic circuit refers to the circuit ability to tolerate noise without causing spurious changes in the output voltage. • A quantitative measure of the noise immunity is called noise margin. Operating Temperature • ALL IC gates are semiconductor devices that are temperature-sensitive by nature. • The operating temperature ranges for and IC vary from 00 C to +700 C for consumer and industrial applications and from -550 C to + 1250 C for military applications Power supply requirements • The amount of power and supply voltage required by an IC are the main parameters to be taken into consideration while choosing a proper power supply The End ……Thank you…… M.S.P.V.L. Polytechnic College, Pavoorchatram.