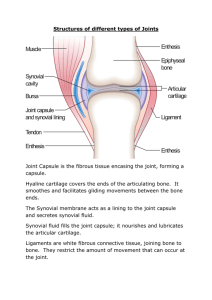
Synovial Joints
advertisement

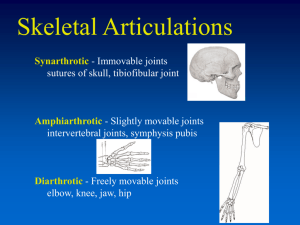
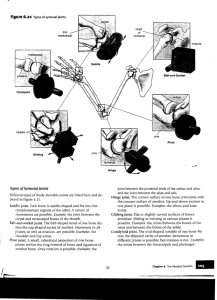
Synovial Joints DIARTHROTIC ARTICULATIONS What are synovial joints? Freely movable joints Contain a cavity filled with thick, slippery fluid (Synovial fluid) Found mostly in articulations of the appendicular skeleton Articular Cartilage Covers the ends of bones Made of hyaline cartilage Reduces friction between bones Cartilage wearing away causes pain and restricted motion Types of synovial joints: Gliding (plane) Pivot Hinge Ball and socket Elipsoid (Condyloid) Saddle Gliding or Plane joints: Formed between 2 opposing flat surfaces Bones slide over each other Pivot Joints: Rotation around an axis Hinge Joints: Part of one bone fits into a convex cavity in another bone. Motion is in one plane, back and forth Ball-and-Socket Joint A round projection on one bone (head) fits into a depression (socket) on another bone. Allows a wide range of motion Easy to dislocate Ellipsoid (Condyloid) Joints: Modified ball and socket joints in which the head of a bone is similar in shape to a football Moves in two axes, but restricts rotational motion Saddle Joints Made by 2 saddle-shaped surfaces at right angles to each other The Knee Joint THE ARTICULATION OF 3 BONES Bursa/e – Sacs filled with synovial fluid for cushioning ACL and PCL – Ligaments that connects the tibia to the femur Meniscus – crescentshaped fibrocartilage pads that help cushion joints The Knee A modified hinge joint Allows flexion, extension, and limited rotation Knee dislocation – owww! Chicken Leg Dissection EXAMINATION OF THE KNEE JOINT