Major Bones and joints
advertisement

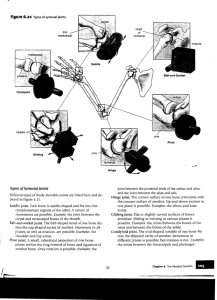
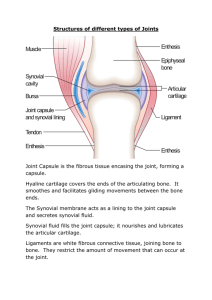
Core 2: The body in motion Focus Question 1: How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? Students learn about: skeletal system Students learn to: identify the location and type of major bones involved in movement, eg long bones articulate at hinge joints for flexion and extension. • Major bones involved in movement: Types of synovial joints • Gliding joints: side-to-side or back-and-forth movements usually across flat surfaces. Example: between carpals and tarsals • Hinge joints: the convex curve of one bone fits into the concave surface of the other. Movement in one plane. Example: elbow and knee joints. • Pivot joint: primary movement is rotation. The rounded/pointed surface of one bone joins with the depression of another bone. Example: between atlas and axis, or at the proximal end of the radius and ulna. Synovial joints cont • Ellipsoid joint: oval-shaped condyle of one bone fits into the elliptical depression of another. Movement in two planes. Example: joints between metacarpals and phalanges. • Saddle joint: one bone is saddle-shaped and the other bone sits like a rider. Example: carpal and metacarpal of the thumb. • Ball and socket joint: one round ball joint fits into a cup-like depression of another. Example: shoulder and hip joint