Joint
advertisement
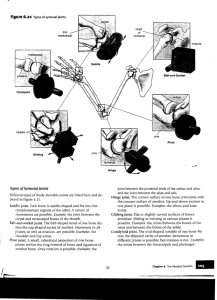
ARTICULATIONS WHAT IS A JOINT? • A site where two or more bones meet. • Provides mobility • Weakest point of skeleton Joint Structure • Fibrous connective membranes • Sutures – connected by short fibers from the periosteum (becomes synostosis in adult) • Syndesmoses – connected by ligaments (distal end of tibia & fibula) • Gomphoses -- “peg in sockets” (tooth sockets) Joint Structure • Cartilaginous - hyaline cartilage holding joint together • Synchondroses– cartilage unites bones (epiphyseal plates & costal joints) • Symphyses – connected by fibrocartilage (pubic symphysis, vertebral joints) Joint Structure • Synovial joints – separated by a fluid containing joint cavity • Diarthroses - freely moveable joints such as shoulder, knee, hip, and most others Joints classified by function • Synarthroses –NO MOVEMENT • (sutures, gomphoses, synchondroses, some syndesmoses) • Amphiarthroses – –SLIGHT MOVEMENT • (symphyses, some syndesmoses Joints by function • Diarthroses - FREELY MOVABLE • Plane (gliding) - tarsals and carpals • Condyloid (ellipsoid) – metacarpophalangeal joints • Pivot - Atlas/Axis; Radius/Capitulum • Saddle - Thumbs • Hinge – Elbow, Knee • Ball and socket – Shoulders, Hips Suture Synchrondroses Syndesmosis Symphyses Synovial Joint Ball & Socket Joint Condyloid Joint Hinge Joint Pivot Joint Saddle Joint Plane (Gliding) Joint Structure of Diarthrotic Joint • Two or more opposing bones • Joint capsule of connective tissue surrounds joint cavity • Joint cavity lined with synovial membrane • Articular cartilage – covers ends of bone • Menisci (articular disks) - cartilage pads (knee) • Bursae – flattened sacs filled with synovial fluid • Ligaments – attach bone to bone • Tendons – attach muscle to bone Synovial Joint Types of Movement • • • • • Flexion/Extension Abduction/Adduction Circumduction Rotation Protraction/Retraction Protraction / Retraction Types of Movement • • • • Elevation/Depression Inversion/Eversion Pronation/Supination Dorsiflexion/Plantar flexion Supination / Pronation Elevation / Depression Inversion / Eversion Joint Injuries • Sprains - ligaments stretched or torn • Cartilage Injuries - torn cartilage rarely repairs because it’s avascular) • Dislocations (luxation) - bones moved out of alignment Knee Joint Inflammatory/Degenerative Conditions • Bursitis - inflammation of a bursa caused by blow or friction • Tendonitis - inflammation of tendons caused by overuse • Arthritis Arthritis – >100 different types; affecting 1 out of 7 –Osteoarthritis - Wear & Tear; affects 85% –Rheumatoid Arthritis - Autoimmune • May occur at any age; Most common around 40-50; Affects 1-2% of Americans • Immune cells attack joint tissue causing scarring & ossification • Ankylosis = stiff deformed joints –Gouty Arthritis (Gout) • Caused by build up of Uric Acid Other Bone Disorders • Rickets - soft bones; lack of calcium due to vitamin D deficiency • Osteoporosis - excessive bone loss • Paget’s disease - excessive bone formation • Osteomyelitis - Inflammation caused by pusforming bacteria • Achondroplasia - defective endochondral bone growth; form of dwarfism • Osteosarcoma - form of bone cancer • Scoliosis - abnormal lateral curvature of the spine • Kyphosis - abnormal thoracic curvature • Lordosis - abnormal lumbar curvature • Herniated Disk (Ruptured or Slipped Disk) - compression on intervertebral disk presses on nerves