China and the Communist Revolution
advertisement

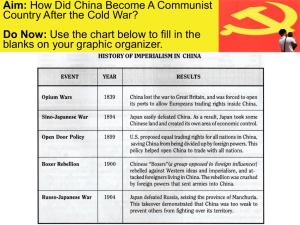
China and The Communist Revolution I. Language A. There are two main languages in China 1. Mandarin 2. Cantonese B. They sound very different from each other and most people only speak one of them. II. Writing All Chinese writing uses the same set of characters. There is no connection between the written and spoken forms of language. III. The End of the Dynasties A. During the last dynasty-Qing Dynasty-the population of China tripled, leading to shortages, famines, and wars. B. Opium Wars between Great Britain and China from 1839 and 1842. 1. Treaty of Nanking 2. China lost Hong Kong to Great Britain and was forced to allow more trade with Great Britain. End of the Dynasties C. Many peasants were angered by the treaty and a rise in nationalism led to Chinese rebellions against the Qing Dynasty. 1. Taiping Rebellion - 14 years - 20 million deaths 2. Boxer Rebellion The End of the Dynasties D. Many western educated Chinese wanted a more modern China with a democratic government. 1. Sun Yat-sen founded the Nationalist Party and overthrew the Qing Dynasty to begin The Republic of China. 2. As the Nationalist Party struggled with the new republic, other political powers began including the communist party. IV. Civil War Chiang Kai-shek leader of Nationalist Party Mao Zedong leader of Communist Party A. The Nationalist Party and the Communist Party had many clashes over the years. B. The Communist Party had to flee to northern China—this is called The Long March. B. The Long March 1. 100,000 people walked 6,000 miles to escape from the Nationalist Party. 2. During The Long March Mao Zedong became the official leader of the party. V. The Nationalist Party A. The Nationalist republic maintained control through 1949. They improved transportation, provided a better education to more people, and encouraged industry. B However, peasants and workers lives were not improved… VI. Communism in China A. In 1949 the Communist Party wins the civil war. B. Mao declares China a communist state called The People’s Republic of China. C. Chiang Kai-shek and the Nationalist Party flee to the island of Taiwan and establish The Republic of China. Chairman Mao October 1, 1949 The People’s Republic of China D. The First Stage of Communism Land was seized from the wealthy and given to the peasants. 2. A five year plan brought all industry under the government’s control. 3. Peasants combined their land to form collective farms. 1. E. The Great Leap Forward 1. Collective Farms became huge communes—25,000 peasants living together! 2. Poor production, droughts, and floods caused one of the worst famines in history. 3. In two years 20 million people starved to death. Terraced Farming – Rice Paddies F. The Cultural Revolution 1. To maintain control Chairman Mao launched the Cultural Revolution to remove opposition to the Communist Party. Cultural Revolution 2. The Cultural Revolution punished people who spoke against communism or the government. Artist were forced to create propaganda supporting communism. VII. Human Rights A. During the years of the Cultural Revolution the economy weakened and the government was unable to perform their duties such as health care and education. B. Many Chinese called for reform. C. Mao Zedong died in 1976 and the Cultural Revolution ended. Human Rights Deng Xiaoping took power in 1977. Opens up diplomatic relations with the west. Continues repression of human rights. President Nixon and Chairman Mao had a historic meeting in 1972. The U.S. had not met with China since 1949. D. Tiananmen Square - 1989 Student protest against human rights abuses.