Cold war Asia Complete - John Bowne High School
advertisement

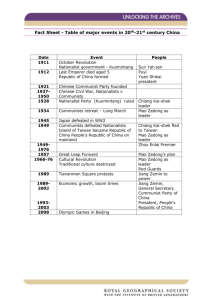
Aim: How Did China Become A Communist Country After the Cold War? Do Now: Use the chart below to fill in the blanks on your graphic organizer. From Imperialism to Republic • For many years, foreign countries controlled China’s trade and economic resources. • Many people, including groups like the Guomintang (or Nationalist Party), led by Sun Yixian believed that modernization and nationalism could restore Cina’s independence. • In 1911, a group called The Revolutionary Alliance, a forerunner of the Guomintang, successfully overthrew the Qing Dynasty, (the last series of emperors from a single family that had ruled China since 1644). After becoming the president of a new Republic of China in 1912, Sun Yixian aimed to establish a modern government by using “three principles of the people”… 1. Nationalism- an end to foreign control 2. Democracy- restoring people’s rights 3. Peoples livelihood- Economic Security for all Chinese From Republic to Revolt •After gaining power, Sun turns over the Presidency to powerful general named Yuan Shikai who rules like an emperor snd ultimately betrays the ideals of the revolution. This sparks local revolts. •After Yuan Shikai’s death (1916), civil war breaks out in China and authority falls into the hands of warlords who rule territories as large as their armies could conquer. World War I increases tension in China •China fights on side of victorious allies but suffers huge casualties during WWI. •After the war, some Chinese leaders felt that the Allies should repay them for their help by returning control of Chinese territories that had previously been controlled by Germany. However, under the Treaty of Versailles, the Allied leaders decided to give these territories to Japan. •On May 4, 1919, outraged students gathered in Beijing to protest Japanese control of colonies in China. This began the May Fourth Movement. It’s supporters aimed to make China stronger through modernization. China splits in two during WWII Communist vs. Nationalists •In 1921, two leaders rise to power and jockey for political control. Jiang Jieshi leads the nationalist party and Mao Zedong leads the Communist party. •At first Nationalists and Communist work together to defeat warlords and unite China but Chiang Kai-shek (aka Jiang Jieshi) sees communist as a threat and he wages civil war between the nationalist and communist in china. •This bitter civil war continues to rage when Japan invades China in 1937. Chiang Kai-shek Dominates the South Mao Zedong Dominates the North The Long March (1934-1935) Chinese communists make a 6000 mile trek from southeastern to northwestern China. This relocates the communist revolutionary base and sets the stage for establishes Mao Zedong to become the undisputed party leader. World War II in China During WWII, the Nationalists and Communist temporarily unite to fight the Japanese. But they continued to jockey for position within China. After Japan surrenders in WWII, Civil war between Nationalists and Communists resumes. This renewed civil war lasts from 1946 to 1949. In 1949, Mao Zedong gains control of the country and proclaims it the peoples Republic of China. Chiang Kai-shek and other Nationalist leaders retreat to the island of Taiwan. Reasons for Communist Success: 1. Communist promised to distribute free land to China’s poor and landless peasant farmers (90% of the population). Most farmers supported the Communist rebels. 2. The Soviet Union provided money, weapons, and training to the communist rebels. 3. The Chinese Nationalist government was incompetent, corrupt and too weak to stop Mao Zedong’s forces. The existence of two China’s increases tensions between the Superpowers during the Cold War The U.S. supports Chiang Kai-shek and helps him set up a Nationalist govern-ment called the Republic of China. The Soviets support Mao Zedong and the countries pledge to assist one another if either is attacked.