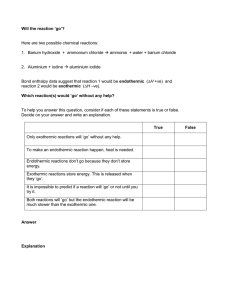
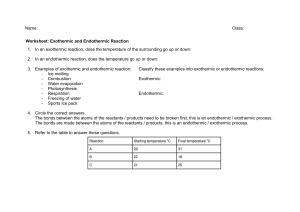
Endothermic processes: 1. Energy absorption: Endothermic processes absorb energy (heat) from their surroundings. 2. Temperature change: These processes result in a decrease in temperature of the system as energy is taken in. 3. Bond formation: Generally, endothermic processes involve breaking bonds, which requires energy input. 4. Enthalpy change: In endothermic reactions, the enthalpy change (∆H) is positive. Example: Melting of ice or photosynthesis in plants. Exothermic processes: 1. Energy release: Exothermic processes release energy (heat) to their surroundings. 2. Temperature change: These processes result in an increase in temperature of the system as energy is given out. 3. Bond formation: Generally, exothermic processes involve forming bonds, which releases energy. 4. Enthalpy change: In exothermic reactions, the enthalpy change (∆H) is negative. Example: Combustion of fuels or cellular respiration in living organisms.