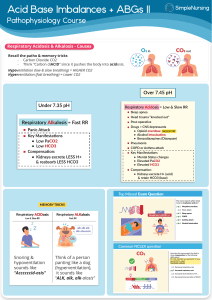
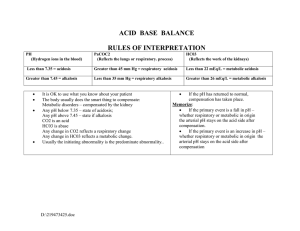
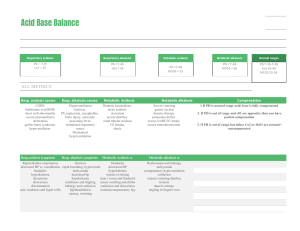
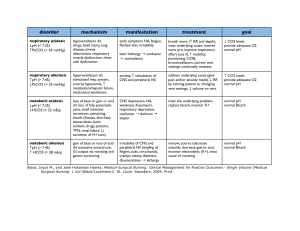
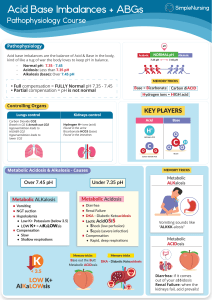
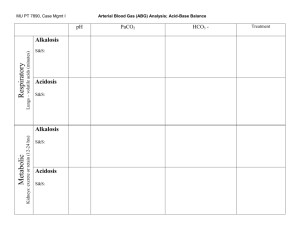
6 Easy Steps to ABG Analysis 1. 2. 3. 4. Is the pH normal? Label it Is the CO2 normal? Label it Is the HCO3 normal? Label it Does the CO2 or the HCO3 go in the opposite direction? If yes, then there is compensation 5. Are the pO2 and O2 saturation normal? If no, then they are hypoxic Test pH pCO2 HCO3 pO2 O2 saturation Normal 7.35-7.45 35-45 mmHg 22-26 Meq/L 80-100 mmHg 98-100% ↓Value Acidosis Alkalosis Acidosis Hypoxemia Hypoxemia ↑Value Alkalosis Acidosis Alkalosis ROME Respiratory Opposite (arrows are opposite) Metabolic Equal (arrows are equal) Ex: pH 7.50 CO2 30 = respiratory alkalosis (breathing too fast, blowing co2 too fast, causing anxiety, pain, fever, infection, hyperventilation) Respiratory is quickest avenue for compensation Pain, fever, infection will increase respiratory rate and increase chance to getting respiratory alkalosis. pH 7.31 acidosis CO2 48 = respiratory acidosis (hypoventilation, atelectasis, trauma, narcotics) could be respiratory arrest, pain, CNS depressants pH 7.20 - CO2 36 HCO3 14 Metabolic acidosis (cardiac arrest patients), patients who have GI problems – diarrhea = IBD pH 7.47 CO3 45 HCO3 33 Metabolic alkalosis (GI loss from vomiting or emesis, NG tube suction)