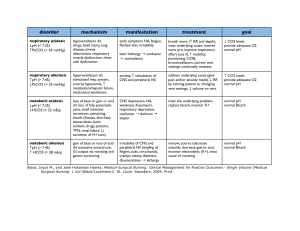
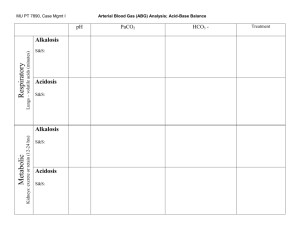
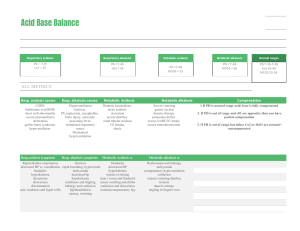
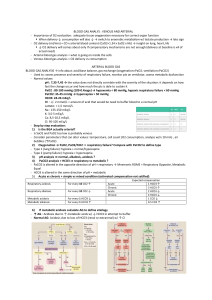
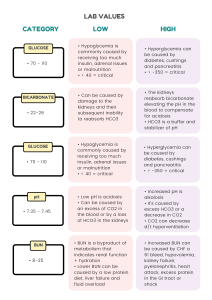
Acid Base Imbalances + ABGs II Pathophysiology Course Respiratory Acidosis & Alkalosis - Causes O2 in Recall the patho & memory tricks - Carbon Dioxide CO2 - Think “Carbon diACID” since it pushes the body into acidosis. CO2 out Hypoventilation (low & slow breathing) = HIGHER CO2 Hyperventilation (fast breathing) = Lower CO2 Over 7.45 pH Under 7.35 pH Respiratory Acidosis = Low & Slow RR Sleep apnea Respiratory Alkalosis = Fast RR Panic Attack Key Manifestations • Low PaCO2 • Low HCO3 Compensation: • Kidneys excrete LESS H+ & reabsorb LESS HCO3 Head trauma “knocked out” Post-operative Drugs = CNS depressants • Opioid overdose NCLEX TIP • Alcohol intoxication • Benzodiazepines (Diazepam) Pneumonia COPD or Asthma attack Key Manifestations • Mental Status changes • Elevated PaCO2 • Elevated HCO3 Compensation: • Kidneys excrete H+ (acid) & retain HCO3 (base) Top Missed Exam Question The nurse expects which client to be in respiratory acidosis? MEMORY TRICKS Respiratory ACIDosis Low & Slow RR 1. Morphine overdose pH Respiratory ALKalosis Respiratory ACIDosis Fast RR 2. Panic attack 3. Sleep apnea 4. COPD 5. Asthma attack 6. Alcohol intoxication alk alk alk alk-alooosis CO2 Common NCLEX question CO2 How does the nurse expect the client to show compensation for the following ABG values? Ph 7.20, PaO2 82 mm Hg, PaCO2 37 mm Hg, HCO3 15 mEq/L (metabolic acidosis) 1. Decreased respiratory rate 5 6 7 8 9 10 13 14 0 1 2 3 4 12 Think of a person panting like a dog (hyperventilation), it sounds like “ALK, alk, alk-alosis” 11 Snoring & hypoventilation sounds like “Accccccid-osis” Acidotic 7.35 pH 2. Increased respiratory rate 3. Increased renal retention of H+… pH NORMAL pH Alkalotic 7.45 pH 4. Decreased renal excretion of HCO3