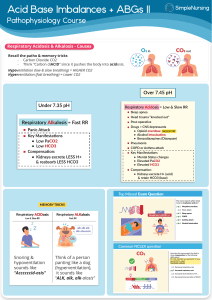
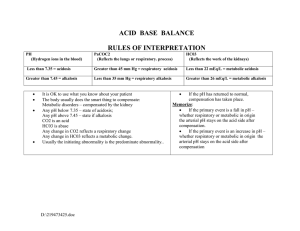
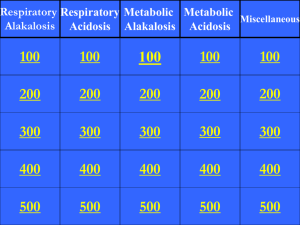
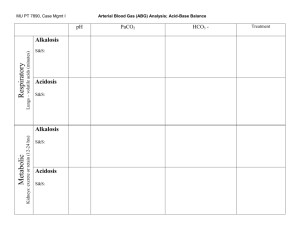
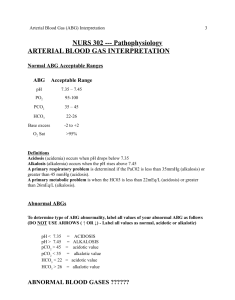
Evaluation 1)ABG Pre test 2)ABG Post Test 3)Informal Feedback of interventions/patient safety related to scenario 4)Demonstration on clinical area ABG Pre Test Quiz 1. Briefly describe what ABG’s mean from a physiologic perspective (Small group discussion) 2. List three factors that can affect ABG’s.(Small group discussion; also explore possible physiological interactions) 3. Group practice calculate the following ABG’s and determine if they are normal, respiratory acidosis, respiratory alkalosis metabolic acidosis or metabolic alkalosis. Partially compensated, uncompensated, fully compensated. Pre-Test and Post-Test Matching 1. ______pH = 7.576, CO2 = 28, HCO3 = 25 2. ______pH = 6.96, CO2 = 71, HCO3 = 26 3. ______pH = 7.51, CO2 = 9, HCO3 = 7 4.______pH = 7.16, CO2 = 82, HCO3 = 29 5.______pH = 6.68, CO2 = 86, HCO3 = 10 6.______pH = 7.76, CO2 = 28, HCO3 = 40 7.______pH = 7.32, CO2 = 68, HCO3 = 36 8.______pH = 7.365, CO2 = 40, HCO3 = 23 9.______pH = 7.49, CO2 = 19, HCO3 = 16 10.______pH = 7.20, CO2 = 62, HCO3 = 19 Answer Choices: A) Normal B) Respiratory Acidosis C) Compensated Metabolic Acidosis D) Partially Compensated Respiratory Acidosis E) Combined Acidosis F) Respiratory Alkalosis G) Combined Alkalosis H) Partially Compensated Respiratory Alkalosis Post Test Correct Answers 1. F 2. B 3. H 4. D 5. E 6. G 7. D 8. A 9. H 10.E Post-test Patient Scenario A 60 year-old man with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is admitted to s medical unit. His family are concerned, they report to the nurse he is more somnolent than normal. On further history, it is noted the patient has been having problems with morning headaches and often seems exhausted when he wakes up. His thinking is slow and he reports to them he is not refreshed. Acid-base status review: • The patient has a low pH (acidemia) • The PCO 2 is high (respiratory acidosis) and the bicarbonate is high (metabolic alkalosis). The low pH in combination with the high PCO 2 Assessment Respiratory acidosis is the primary process. The metabolic alkalosis is the compensatory process. Summary: A chronic respiratory acidosis with a compensatory metabolic alkalosis. Alveolar-arterial oxygen difference: The alveolar-arterial oxygen difference is 9 mmHg, a normal value, which tells us that the hypoxemia is entirely due to hypoventilation. Explanation for the clinical picture The patient has a respiratory acidosis with a compensatory metabolic alkalosis. The respiratory acidosis tells us that the patient is hypoventilating while the compensatory metabolic alkalosis tells us that this is a chronic process. The patient is likely hypoventilating due to progression of his amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, a neurodegenerative disorder associated with progressive muscle weakness that eventually involves the muscles of respiration. 3) Safety and Quality Principals: Small group discussion questions. Introduction to discussion: Continuous quality improvement encourages a culture of inquiry, welcomes question, investigates outcomes and critically analyzes incidents. Based on the scenario, discuss the questions below with your group. Have a group leader write your answers on the flip chart provided. * It is important to educate the patient and family about respiratory health and warning signs of respiratory distress; how would you do this? * You call the respiratory therapy to reinforce education, he replies he is too busy to see the patient prior to discharge. How would you encourage reinforcement of quality and safe care if this occurs? * Your health assessment the next day confirms the patient is now respiratorily compromised. You report this to your chief nurse, she replies the on call MD never answers his phone, just monitor the patient. What other action could you take to provide the patient with quality and safe care? (see considerations below) Interventions/Considerations of safe care may include putting patient on CPAP if already ordered, intermittent bagging to increase ventilation, and calling attending or alternate physician if on-call resident doesn’t answer. Due to his diagnosis, his condition will not improve by encouraging patient to ‘take deep breaths’.