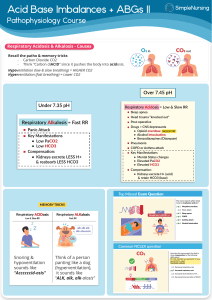
Respiratory Acid – Base Balance: Operates FAST, in a matter of
advertisement

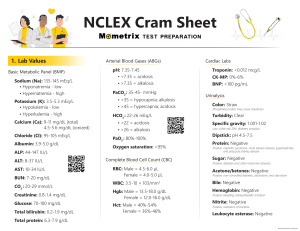
MU PT 7890, Case Mgmt I Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Analysis; Acid-Base Balance pH Lungs – volatile acids (minutes) Respiratory Alkalosis S&S: Acidosis S&S: Kidneys: excrete or retain (12-24 hrs) Metabolic Alkalosis S&S: Acidosis S&S: PaCO2 HCO3 - Treatment Acidemia can occur from 2 different causes: 1. Respiratory cause: ↑PaCO2 [an INVERSE relationship to the pH] The CO2 dissolved in blood is carbonic acid (H2CO3). CO2 remains a “volatile” gas that can be “blown off” during expiration. High PaCO2 (hypercapnia) is caused by alveolar hypoventilation that is the result of either thickened, scarred alveolar wall, excessive secretions, or destruction of the alveolar surface area that is available for diffusion of O2 and CO2. Therefore less CO2 can be blown off. It makes the blood more acidic, lowering the pH. S&S: dyspnea, anxiety, headache; if acute it can progress to confusion and coma Rx: address the Ventilation : Perfusion mismatch (V:Q < 1) by airway clearance techniques; also by pursed lip breathing to provide positive airway pressure (PAP) to splint open the bronchioles and alveolar ducts; stop exposure to environmental triggers / smoking 2. Metabolic cause: ↓ HCO3 (and ↓PaC02) [a DIRECT relationship to the pH] The Bicarb ion is being used up to buffer the non-volatile acids circulating in the blood, i.e. lactic acid from anaerobic metabolism, ketones from incomplete fat metabolism, or ketones from diabetic hyperglycemia / ketoacidosis. S&S: Kussmaul breathing (secondary hyperventilation that is variously described as “deep, rapid, labored, sighing”), nausea; can progress to coma Rx: safe exercise and activity to minimize lactic acid production; proper nutrition to prevent ketoacidosis. Diabetics must manage blood sugars more tightly. Alkalemia can occur from 2 different causes: 1. Respiratory cause: ↓ PaCO2 [an INVERSE relationship to the pH] Hyperventilation: over-ventilation that blows off too much CO2 due to anxiety, pain, or cerebral trauma S&S: dizziness, syncope, N&T, early tetany Rx: Treatment of respiratory alkalosis includes reassurance, assistance in slowing breathing and facilitating relaxation, sedation, pain control, CO2 administration, and use of a rebreathing device such as a rebreathing mask or paper bag. A rebreathing device allows the client to inhale and “rebreathe” the exhaled CO2. Teach diaphragmatic breathing. 2. Metabolic cause: ↑ HCO3 (and ↓PaC02) [a DIRECT relationship to the pH] Multiple causes: eating too many antacids, excessive vomiting loses stomach acid, other reasons. S&S: weakness, mental dullness, early tetany Rx: educate on antacid use