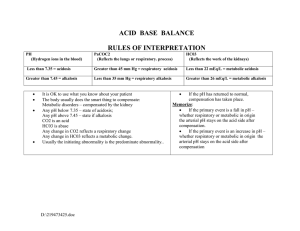
ACID-BASE IMBALANCE ACIDOSIS (pH<7.35) Metabolic Characteristics Mechanism >concentration of noncarbonic acids. Bicarbonate loss Results when the normal buffer system is compromised and bicarbonate to carbonic acid ratio decreases to < 20:1 For Increased non-carbonic acids :- ketoacidosis; lactic acidosis; ingestion; uremia; distal renal tubule acidosis. For Hyperchloremic Acidosis :- Diarrhea; renal failure; proximal renal tubular acidosis Causes Symptoms Headache, lethargy, confusion, coma Respiratory Alveolar hypoventilation. Hypercapnia Results form the decreased alveolar ventilation in relation to the CO2 metabolic production Depression of the respiratory centre; paralysis of the respiratory muscles; disorders of the chest wall; disorders of the lung parenchyma Headache, blurred vision, breathlessness, restlessness, lethargy, disorientation, muscle twitching, tremors, convulsions, coma ALKALOSIS (pH>7.35) Metabolic Loss of metabolic acids. excess Bicarbonate Ineffective renal compensation as loss of chloride stimulates bicarbonate retention. Hyperaldosteronism; use of diuretics Respiratory Alveolar hyperventilation. Hypocapnia The reduced C)@ plasma levels lead to decreased carbonic acid concentration Hypoxemia; hypermetabolic states; early salicylate intoxication; hysteria; cirrhosis; gram negative sepsis; improper ventilator use Dizziness, confusion, Weakness, muscle tingling of extremities, cramps, hyperactive convulsions, coma, reflexes, tetany, symptoms of confusion, convulsions, hypocalcemia like tetany atrial tachycardia, and carpopedal spasm. hypocalcemia Reference El-Hussein, M., T.; Power-Kean, K.; Zettel, S., (2018, March). Understanding Pathophysiology (Canadian ed.). Elsevier.