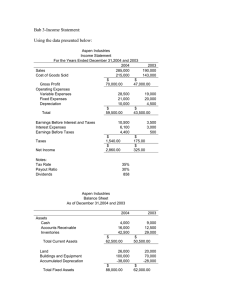
The 5 Account Types: 1. ASSETS - all useful or valuable things that the company owns. - ex: cash, cars, buildings, land, etc. 2. LIABILITIES - a company's legal financial debts or obligations. - payable in the future - ex: accounts payable, unearned revenue 3. EQUITY - the value of an owner's interest in a company. - accounts in this category are: common stock, retained earnings, and dividends. 4. REVENUES - money earned through services provided or goods sold by the company. 5. EXPENSES - money spent by a company to generate revenues (cost of doing business.) - ex: rent expense, utilities expense, wages expense, etc. * net income: revenues are greater than expenses * net loss: expenses are greater than revenues 1 FINANCIAL STATEMENTS There are four fundamental financial statements used in accounting: 1. INCOME STATEMENT Describes a company’s revenues and expenses along with the resulting net income or loss over a period of time due to earnings activities. 2. STATEMENT OF RETAINED EARNINGS Reconciles the beginning and ending retained earnings for the period, using information such as net income from the Income Statement. 3. BALANCE SHEET Describes a company’s financial position (types and amounts of assets, liabilities, and equity) at a point in time. 4. STATEMENT OF CASH FLOW Identifies cash inflows (receipts) and cash outflows (payments) over a period of time. * The first financial statement that we prepare is the income statement. 2 Assets Dividends * these accounts have a normal DEBIT balance. Expenses DEBIT increases the account balance. CREDIT decreases the account balance. Liabilities Retained Earnings & Common Stock * these accounts have a normal CREDIT balance. Revenues DEBIT decreases the account balance. CREDIT increases the account balance. T-ACCOUNT 3