7 Grade Lit Terms Genre
advertisement

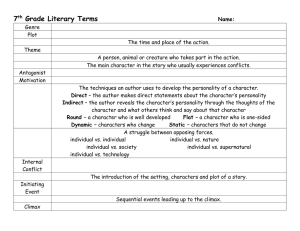
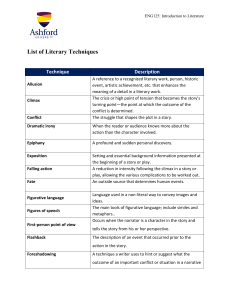
Genre Plot Setting Theme Characters Protagonist Antagonist Motivation Characterization 7th Grade Lit Terms A category or type of literature – Prose, Poetry and Drama The sequence of events in a literary work. (the action or events in a story) The time and place of the action. The central message or insight the author wants us to learn. The moral of the story. A person, animal or creature who takes part in the action. The main character in the story who usually experiences conflicts. The character that opposes the main character. The driving force behind a character’s actions or thoughts The techniques an author uses to develop the personality of a character. Direct – the author makes direct statements about the character’s personality Indirect – the author reveals the character’s personality through the thoughts of the character and what others think and say about that character Round – a character who is well developed Flat – a character who is one-sided Internal Conflict Exposition Initiating Event Dynamic – characters who change Static – characters that do not change A struggle between opposing forces. individual vs. individual individual vs. nature individual vs. society individual vs. supernatural individual vs. technology A struggle inside a character. The introduction of the setting, characters and plot of a story. The introduction to the central conflict in the story. Rising Action Climax Falling Action Resolution Dialogue Sequential events leading up to the climax. The turning point in the story where the problem is at its worse. Sequential events that tie up loose ends and begin to resolve the conflict. The new norm. What happens in the end. The words spoken by characters in a literary work. Flashback The action that interrupts to show an event that happened at an earlier time which is necessary to better understanding. The use of hints or clues to suggest what will happen later in literature. The vantage point from which the story is told. First person – the story is told by a character. Third person – the story is told by a narrator who is not a character in the story. Third person omniscient – the narrator tells the story through all the characters’ feelings and thoughts. Third person limited omniscient – the narrator tells the story through only one character’s feelings and thoughts. The conflict between expectation and reality; between what is said and what is meant; between what appears to be true and what really is true. The attitude a writer takes towards a subject or character. The feeling created in the reader by a literary work. Repetition of final consonant sounds Repetition of vowel sounds External Conflict Foreshadowing Point of View Irony Tone Mood Consonance Assonance