LITERARY ELEMENTS
advertisement

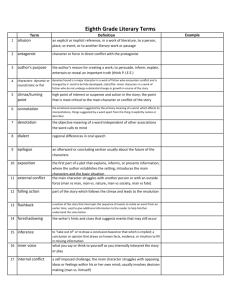
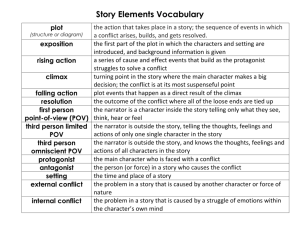
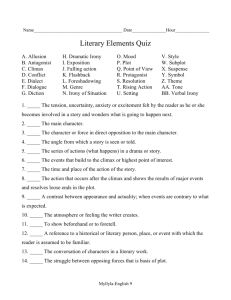
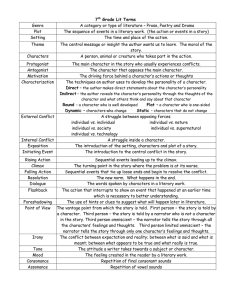
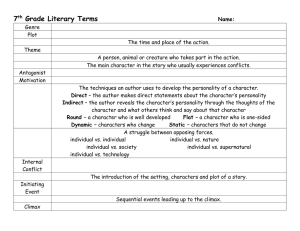
LITERARY ELEMENTS ELEMENTS OF A STORY AKA the Plot Pyramid Plot= sequence of events in a story. EXPOSITION The background information of a story Introduces setting, situation and characters Inciting incident Sparks the conflict; event that sets the conflict into motion CONFLICT Major problem of the story that must be solved by the end. Struggle between opposing forces: external and internal. RISING ACTION The events of a story building suspense What leads up to the climax CLIMAX The turning point of the story Highest point of emotional intensity (for characters!) FALLING ACTION The events winding down in the story Leading towards the resolution RESOLUTION The final outcome of a story resolves the major conflict of the story Terms Essential for Telling and Understandi ng Short Stories THEME A central idea or statement that unifies and controls and entire literary work. Basically, the moral or message of the story. Must ALWAYS be in sentence form. NEVER just one word. SYMBOLS A word, place, character, or object that means something beyond what it concretely means. EX: a dove =peace IMAGERY Creating“mental pictures” by using lots of colorful language that actually paints a vision, employing your five senses. EX: The sun erupted from its slumber showering the morning with blazing shades of crimson and burnt orange. TONE Author’s attitude toward a subject Described as an adjective: ex. humorous, angry, delighted, mockserious MOOD The feeling or atmosphere a writer creates in a work. SETTING Time and place of the action of a story. CHARACTERIZATION The way of describing characters and revealing their personalities. DYNAMIC CHARACTER Characters change that undergo STATIC CHARACTER Characters that do not change. Allusion Indirect reference to another literary work or famous person, place, or event. Foreshadowing: Use of hints or clues to indicate events and situations that will occur later in the plot. Creates SUSPENSE and prepares reader for what is to come. Suspense: Excitement or tension readers feel as they become involved in the story and eager to know the outcome. IRONY Difference from what is expected; contrast between appearance and reality. Situational: contrast between what a reader expects and what actually happens. Dramatic: reader knows more than the character Verbal: says one thing means another NARRATION STYLES FIRST PERSON POV The narrator is a character in the story and tells everything in his or her own words. (I) THIRD PERSON LIMITED The narrator tells only what one character thinks, feels, and observes.(he/she) 3rd PERSON OMNISCIENT POV An (omniscient= all-knowing) observer that tells the story and knows it all (almost like a God like character). Sees into the minds of more than one character. I’ll Try not to Torture you with More Notes for a While