7 Grade Pre-AP Literary Terms
advertisement

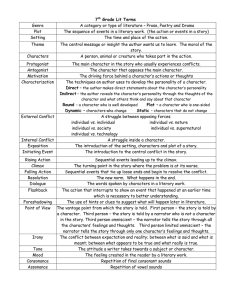
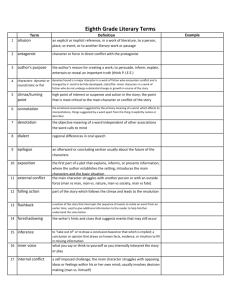
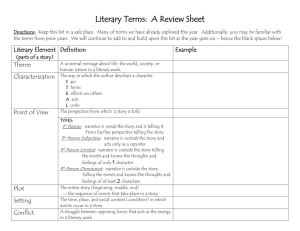
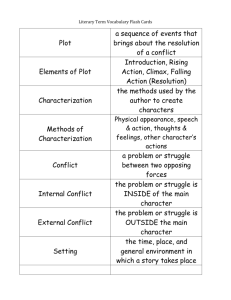
7th RELA 9/24/08 th 7 Grade Pre-AP Literary Terms 1. Character: A person or animal who takes part in a literary work. A. Antagonist: the person/ force/ idea that works against the protagonist B. Protagonist: the central character of a literary work C. Static: a character who has the opportunity to change/mature for better, but chooses not to change. D. Dynamic: a character who changes for the better due to his experiences. 2. Setting: the time and place a literary work takes place. A. Geographical Location: scenery and location. B. Daily Mannerisms: specifics about houses, jobs, entertainment, etc. C. Time Period: the season, historical significance, year, etc. of a story D. General Environment: the social, religious, and educational importance of the setting. 4. Conflict: the problem or struggle in the story. A. Internal: a struggle inside a character Man vs. Himself B. External: a struggle between a character and an outside force. Man vs. Nature Man vs, Man Man vs. Society 5. Point of View: the perspective from which a story is told. A. Participant: a narrator who is a part of the story First Person: told by a character; uses the pronouns I, me, my, we, us, etc. B. Non-participant: a narrator who is NOT part of the story Third-Person Limited: narrator who knows the thoughts and emotions of one of the characters. Third- Person Omniscient: narrator who knows the thoughts and emotions of many or all of the characters. Objective Narrator: narrates the story based on what is seen and heard. 6. Theme: the central idea of a story 3. Plot: the sequence of events of the story, play, novel, etc. A. Exposition: the background information . B. Conflict: the problem or struggle of the story A. Stated: can be found in the story B. Implied: the reader must infer the theme based on what was read. C. Rising Actions: the events leading to the climax of the story 7. Tone: the attitude of the author or speaker towards a subject. D. Climax: pivotal point, the highest point of excitement, of the story 9. Genre: a type of writing (short story, novel, poetry, etc) E. Falling Action: the action that leads to the resolution or revelation of meaning. D. Resolution: part of the falling action that explains the resolution to the conflict. 8. Mood: the emotional atmosphere of the story 10. Figurative Language: language used to produce images in the reader’s mind . A. Simile: the comparison of two unlike things by using like or as. 7th RELA 9/24/08 10. Figurative Language: (cont’d) B. Metaphor: the comparison of two unlike things without using like or as C. Personification: the giving of human characteristics to nonliving object 18. Connotation: the meaning beyond; the feelings or emotions associated to the word. 19. Diction: word choice. 20. Symbolism: symbols that represent something else. 21. Epiphany: a realization of something; an awakening to some aspect of life. D. Oxymoron: using contradictory words (little giant, sweet tart, wise, fool) 11. Sound Devices: stylistic techniques that convey meaning through sound A. Alliteration: words beginning with the same consonant sounds B. Onomatopoeia: words that sound like their meaning or imitate sound 12. Irony: the opposite happens from what was expected A. Situational: when a situations turns out differently than what was expected. B. Verbal: when a character or narrator says one thing while meaning the opposite C. Dramatic: when a character or speaker does not understand something that the audience fully understands or knows. 13. Dialogue: the spoken words between characters 14. Hyperbole: exaggeration 15. Motif: a pattern, strand of imagery, or symbol that recurs throughout a piece of literature. 16. Imagery: description involving the five senses. 17. Denotation: the actual meaning of a word. 22. Foreshadowing: clues or hints given by the author in a story of events to some. 23.Flashback: an interruption in a narrative that goes back and tells of events that happened before that point.