Introduction to Communications Vocabulary Communication:
advertisement

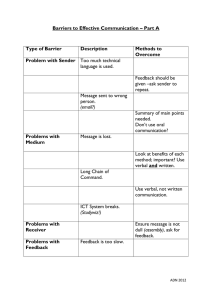
Introduction to Communications Vocabulary 1. Communication: The process of sending and receiving messages. Communication reaches us by means of our sight and hearing and sometimes by our smell, taste, and touch. The Communication Model Sender Feedback---Noise---Message Receiver The Communication Process: 2. Sender: The one who transmits/sends the message. 3. Receiver: The one who interprets or receives the message (decodes message). 4. Medium: The “how”—the communication method (verbal, nonverbal—TV, radio, newspaper, computer, etc.) 5. Message: Words, body language, or symbols that convey (send) an idea or information. Intended: Made up of the meanings and feelings one person wishes to send to another. Actual: What the receiver thinks the sender is actually communicating. Unintended: The message that the sender either does not mean to send or is unaware of sending. 6. Feedback: Reactions (words, body language or symbols) to the message that was received. The response! 7. Noise (Interference): Anything that interferes with communication! Types of Communication: 8. Written: Can be read (books, letters, sign, etc.) 9. Verbal: Spoken—can be heard (talking, radio, TV) 10.Mass Communication: Communication that is created to reach many receivers (TV, magazines, radio, newspapers, internet) 11.Non-Verbal: Sign language; pantomime—mimes, charades; symbols—icons, pictures Note: Effective symbols must be: o Unique—No one else uses it o Appropriate—Relates to the product or service o Memorable—Easy to remember o Recognizable—Easy to identify