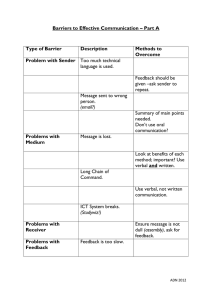
ORAL COMMUNICATION COMMUNICATION COMMUNICATION - exchanging of information, opinion, ideas so that the message is completely understood. 3 FORMS OF COMMUNICATION 1. VERBAL COMMUNICATION - it makes use of our voice (face to face conversations, telephone) 2. NON-VERBAL COMMUNICATION - body language, gestures, postures, facial expressions 3. WRITTEN - emails, book, magazine (written media) 2 TYPES OF CUES 1. VERBAL CUES - prompts conveyed in spoken language a. EMPHASIS CUES - (you need to know. Listen carefully.) b. ORGANIZATIONAL CUES - ( The topic is. First,second. As a result) c. MANNERISM CUES- (repeat, spells important words, speak slowly) 2. NON-VERBAL CUES - prompts that do not use words but rather body language, gestures, postures, facial expression a. KINESICS - certain body movements and gestures serves as form of non verbal communication ( eye contact, posture, facial expression) (shout, cry, laugh) b. HAPTICS - communication by touch ( shakehands, patting someone on back) MODELS OF COMMUNICATION COMMUNICATION PROCESS - transmission or passage of information or message from the sender through a selected channel to the receiver overcoming barriers. ELEMENTS OF COMMUNICATION 1. SENDER - the person who conveys or send the message (oral, nonverbal, written language) 2. MESSAGE - the information being transmitted 3. CHANNEL - medium through which the message is being transmitted 4. NOISE/INTERFERENCE - barrier in communication which hinders the senders message to be understood by the receiver 5. RECEIVER - the one who listens and interprets the message 6. FEEDBACK - the response of the receiver COMMUNICATION MODELS 1. LINEAR MODEL - one way process (feedback through effect) - sender the only one who send message 2. TRANSACTIONAL MODEL - 2 way process - specific goal, field of experience (one is knowledgable ), context 3. INTERACTIVE MODEL- 2 way process (continuous communication) can add another topic - physical context(environmental factors), psychological context ( mental and emotional factors) SPEECH CONTEXT SPEECH - is the expression or the ability to express thoughts or feelings by the articulate sounds. CONTEXT - setting in which communication takes place. SPEECH CONTEXT- way people use to communicate and transmit message orally or verbally. TYPES OF SPEECH CONTEXT 1. INTRAPERSONAL COMMUNICATION - communication with oneself. one person where the speaker acts both as the sender and the receiver. (thinking) 2. INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION - communication between and among people establishes personal relationship. a. DYAD COMMUNICATION - 2 people b. SMALL GROUP - 3 to 12 poeple 3. PUBLIC COMMUNICATION - speaker speaks to an audience. Requires sender to deliver or send the message before or in front of a group. (speech 4. MASS COMMUNICATION - media communication (tv,radio, internet) Form of public communication but is mediated, SPEECH STYLES AND TYPES OF SPEECH SPEECH - is the expression of or the ability to express thoughts and feelings by articulate sounds. (formal adress delivered to an audience) SPEECH STYLE - the form of language that the speaker uses which characterized by the degree of formality . TYPES OF SPEECH STYLES 1. FROZEN - very formal settings (law, pledge, anthem, marraige ceremonies) 2.CONSULTATIVE - semi formal communication (most operational) doctorpatient, teacher-student, businessman-client 3. CASUAL - informal communication between group (talking with peers, teachers collaborating) 4.INTIMATE - very close relationship (couple, family, bestfriend, self talk) 5. FORMAL - avoid using slang terms. says something prepared beforehand (sona, speech, teachers discussion, welcome adresses) TYPES OF SPEECH 1. INFORMATIVE - to inform 2. PERSUASIVE - to persuade or convince an audience to believe 3. ENTERTAINING - to entertain, provides pleasure and enjoyme