13 Relevant Costs for Decision Making Chapter
advertisement
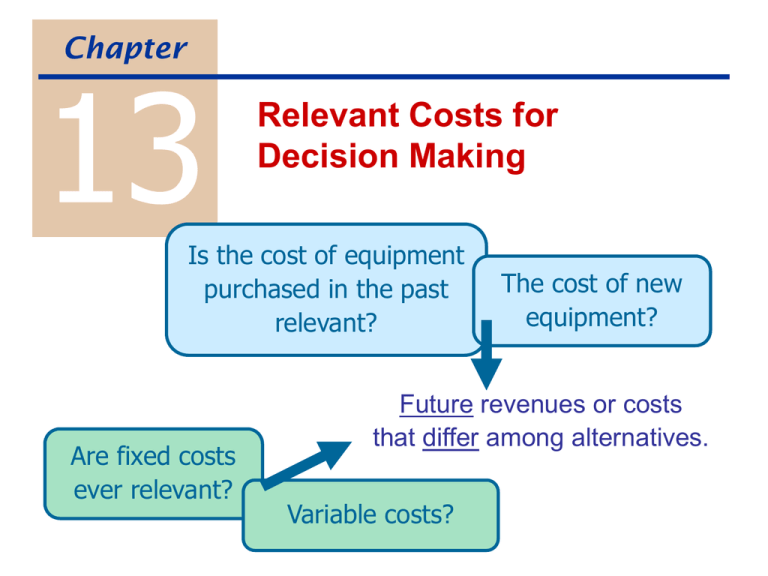
Chapter 13 Relevant Costs for Decision Making Is the cost of equipment purchased in the past relevant? Are fixed costs ever relevant? The cost of new equipment? Future revenues or costs that differ among alternatives. Variable costs? Cost Concepts for Decision Making Avoidable cost or Differential cost important to consider when comparing one alternative to another Sunk cost a cost of the past that cannot be avoided Opportunity cost a benefit (revenue or gain) of an alternative that is not chosen Replacing Equipment The cost of the old equipment is irrelevant. And the loss on the sale of the old equipment is irrelevant. Don’t get trapped by past mistakes! Relevant factors current market value of the old cost & expected life of the new equipment future output future operating expenses Old machine: $50,000 cost, $10,000 accum. depreciation; $7,000 market value New machine: $25,000 cost; 6 year life New machine will decrease annual operating costs from $10,000 to $6,000. Keep Old Oper. Costs (6 yrs) Purchase of new Sale of old Net cash flow Impact of buying new Buy New Adding and Dropping Segments Review Problem, p. 601 Keep Rnd Drop Rnd Revenue $1,000,000 Variable expenses (410,000) Advertising - traceable (216,000) Deprec – special equip (95,000) Supervisor salaries (19,000) General factory OH (200,000) Income $ 60,000 Impact of dropping R.I. Depreciation on equip is irrelevant! Beware of allocated fixed costs! Make or Buy Decisions Exer. 13-9, p. 608 Make Outside purchase DM DL Variable MOH Fixed MOH - traceable Fixed MOH - common Total Impact of outsourcing Some fixed costs cannot be avoided Buy Special Sales Order if regular sales are unaffected, it’s easiest to look at the revenue and costs from special order only Exer. 13-10, Part 1, p. 609 Revenue DM DL Variable MOH Variable selling & adm Additional fixed costs Total effect Special Order Special Sales Order (cont.) Information needed: Number of extra units Selling price per unit Variable cost per unit Changes in fixed costs May need to be calculated. Utilization of a Constrained Resource Exer. 13-5, p. 606 A Sales Variable: DL ($8/hr) Other $ 60.00 B $ 90.00 C $ 80.00 CM per unit Decision based not on CM per unit… … but on CM per constrained resource. Managing Constraints “Bottleneck”: the machine or process that limits overall output Managers should select product mix that maximizes total contribution margin. Managers should try to increase capacity at the bottleneck: working overtime subcontracting of bottleneck process additional investment reducing defects Sell or Process Further Exer. 13-6, p. 606 Sales value after Less: Sales value before Incremental rev / unit A B C $80,000 $150,000 $75,000 Sell or Process Further AgroCorp prepares fruit and vegetable products in a large processing plant. Currently sells 28,000 bags of potatoes @ $2.10. Cost of potatoes=$25,200; cost of package=$0.03; DL=$9,000; MOH= DL x 1.2 = $10,800. Possibility: process the potatoes further to prepare potato flakes. 35,000 boxes of flakes @ $1.80; 14,000 pounds of potato peels @ $0.02 Cost of potato flake box = $0.05 Direct labor cost will increase by $2,000 New rental equipment = $3,200 / year Bags Sales ($2.10 / bag; bag) $1.90 / box) Raw materials Packaging ($.03 / bag) MOH allocated (DL x 1.2) Profit before allocated costs (10,800) $ 12,960 Impact of switching to flakes Beware of allocated fixed costs! Flakes