Ch 1 - UV Part 1
advertisement
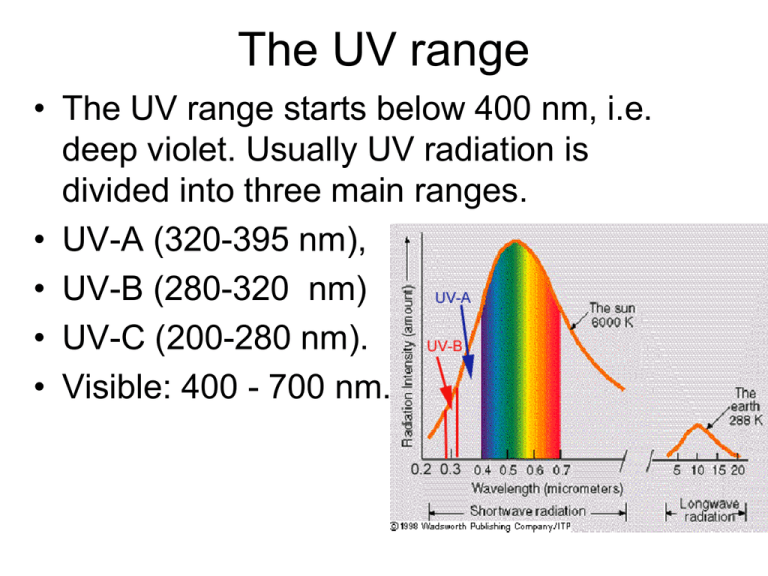
The UV range • The UV range starts below 400 nm, i.e. deep violet. Usually UV radiation is divided into three main ranges. • UV-A (320-395 nm), • UV-B (280-320 nm) • UV-C (200-280 nm). • Visible: 400 - 700 nm. • Book also includes UV-V (visible UV) from 395 to 445 nm. • Also have VUV (vacuum UV) from 100 to 200 nm. – Man-made – Readily absorbed by gases so created in vacuum. – Most small molecules have first transition in this region, so most gases are invisible. Temperature Variations • Regions based on change in temperature. – Troposphere • nearest the Earth • From surface up to about 15 km (10 mi) • Temperature decreases as altitude increases – About 3.5OF (2OC) per 1000 ft. • Atmospheric conditions constantly changing – Weather • About 80% of atmosphere • At the top - Temperature about 45 - 50OC below zero. Regions of the Atmosphere • Stratosphere – strato - layered – 15 to 50 km – Troposphere and stratosphere about 99.9% atmospheric mass. – Non-uniform increase to about 50 km (30 mi) • Mesosphere – Uniform decrease in temperatures again. – 50 km to 100 km (30 mi to 60 mi) • Thermosphere – Temp increases, dependent on Solar activity. Ozone and Ion concentrations • Ozone (O3) – Formed by reactions of oxygen – O2 + energy → O + O – O + O2 → O3 • Dissociation energy comes from the Sun. – Ultraviolet radiation • Optimum conditions about 40 km (25 mi) • O3 concentration decreases to about 70 km (45 mi) Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere Ozone • Region below 75 km known as ozonosphere – Roughly corresponds to stratosphere. – Formed by reaction of molecular oxygen • O2 + energy O + O; then O + O2 O3 – Energy for temp increase comes from ozone absorbing UV radiation! • Causes O3 → O2 + O; and O3 + O → 2O2 • Creates balance of ozone / oxygen in atmosphere. – Pollutant at the Earth’s surface • Also relatively unstable at the surface. Ozone and Ion Concentrations • Serves as ‘umbrella’ for uv radiation. – Greatly decreases uv radiation that makes it to the surface of the Earth. • Upper atmosphere: – N2 + energy → N2+ + e– Ionosphere – Made up of 3 layers Ionosphere • D layer – Absorbs some lower frequency radio waves – Allows higher (AM and FM) frequencies to pass. • E and F layer – Reflect AM – Allow FM to pass Ionosphere • Can use for long distance communication. – Not as reliable as satellite communication – Ionosphere layer will vary with solar activity. Ionospheric Effects • Auroura Borealis – Northern lights – Recombination of ions with electrons – Directed by Earth’s magnetic field – Auroura Australis – AurB2.mpg – http://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=qIXs6Sh0 DKs