Environmental Geochemistry
advertisement

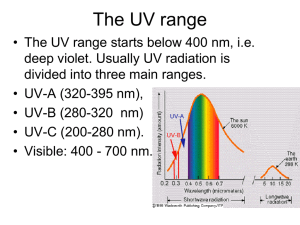
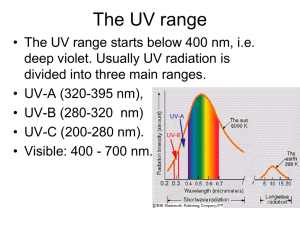
Environmental Geochemistry I- Atmosphere Structure and composition of the Atmosphere Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, and Thermosphere (Fig. 1). Temperature variation in atmosphere (Fig. 1). Composition (Table 1). The ozone hole Effects of ultraviolet radiation on the atmosphere Types of ultraviolet radiation Effects of UV radiation on the biosphere Absorption of UV rays (Fig. 2) Ozone in the stratosphere and effect of CFC’s Ozone hole above Antarctica: Why Antarctica The Greenhouse Effect: Effects of infrared radiation Global warming gases Global warming potentials and residence times (Tables 2 & 3). II- Hydrosphere A- Groundwater Sources of contamination: 1. Industry 2. Septic tanks 3. Landfills 4. Chemical spills 5. Mining 6. Highway deicing salts 7. Agriculture 8. Atmospheric contaminants 9. Radioactive waste. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Attenuation mechanisms: Dilution Dispersion Mechanical filtration Volatilization Ion exchange Biodegradation Radioactive decay Groundwater remediation: (very expensive!) 1. Identify the source 2. Risk- based corrective action: must monitor all the time. 3. Remove or isolate the contaminant: Source control measure (check example on landfills in text) 4. Pump & treat plume 5. Natural and enhanced bioremediation B- Surface water Industrial contamination: organic and inorganic compounds Agricultural contamination C- Oceans and Coastal contamination Residence times: Conservative and non-conservative elements CO2 levels and their “anticipated” effects on the buffer capacity of oceans Oil spills Waste III- Biosphere A. “Endogenous” vs. “Exogenous” elements (Table 4) B. Absorption, Distribution & Excretion C. Toxicity of Metals D. Toxic levels (Fig. 3) E. Neurotoxins: 1. Hg Central nervous system through diffusion 2. Pb Degenerative brain disease; learning disabilities in children 3. Al Alzheimer’s and Dementia. Renal Toxins: 1. U Kills some kidney cells responsible for reabsorption of glucose, amino acids, and some proteins. 2. Cd, Pb & Hg damage cells, inhibit reabsorption of Na 3. Pt Kidney damage and renal failure. Carcinogens: Ni and Cr respiratory cancers Dermatological disorders: Ni, Cr, Be, Co, Au, and Pt. Hazards of Minerals: Asbestos: Crocidolite vs. Chrysotile Uraninite Kidney stones and pancreatic stones: “Biominerals” (Table 5).