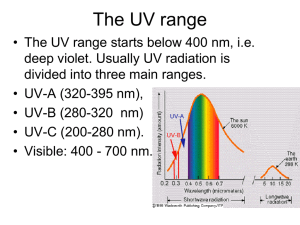
AP Environmental Science Air Pollution, Climate Change, & Ozone Depletion Unit Test Name: _________________________________________________ SID# ________ Questions 1-3 refer to the following regions of Earth’s atmosphere. (a) Thermosphere (b) Exosphere (c) Troposhpere (d) Mesosphere (e) Stratosphere 1. The phenomenon causing global warming occurs primarily in this region of the atmosphere. ____ 2. The beneficial ozone layer is in this region of the atmosphere. _____ 3. Most oxygen is found in this layer of the atmosphere. _____ Questions 4-6 refer to the gases listed below. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) H2O CO2 CH4 O3 CCl2F2 4. A greenhouse gas that is exclusively anthropogenic ________ 5. The most abundant nonanthropogenic greenhouse gas ________ 6. A greenhouse gas that, in the lower troposphere, is formed by photochemical reactions ________ Questions 7-8 refer to the following air pollutants. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Sulfur dioxide Lead Ozone Hydrocarbons Particulates 7. Most often cited as the causative factor for acid deposition ________ 8. Considered harmful in the troposphere but beneficial in the stratosphere APES ________ Pg. 1 Questions 9-12 refer to the layers of Earth’s atmosphere in the temperature profile shown below. 9. Region where the protective ozone layer is located ________ 10. Region that contains the majority of molecules in the atmosphere ________ 11. Region largely responsible for the weather experienced at the Earth’s surface 12. Region with the lowest atmospheric pressure ________ ________ Questions 13-16 refer to the substances listed. (a) Asbestos (b) Radon (c) Lead (d) Carbon monoxide (e) Formaldehyde 13. Found in old plumbing pipes and fixtures and some ceramic glazes ______ 14. Composed of fibers known to cause lung disease ______ 15. Emitted from most manufactured building materials and furniture ________ 16. Colorless, odorless gas that is naturally occurring decay product of uranium ______ APES Pg. 2 Questions 17-18 refer to the following graph. 17. The data in the graph can be useful in explaining the greenhouse effect when they are compared with a. b. c. d. e. volcanic activity sunspot activity mean global temperatures annual nitrous oxide production cycles of flooding and drought 18. The annual fluctuation in carbon dioxide concentration can best be explained by the a. b. c. d. e. seasonal use of fossil fuels regularity of volcanic activity deforestation in the tropics El Nino events seasonal photosynthetic activity of green plants 19. Which of the following is true of carbon as it cycles in nature? a. Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis. b. Carbon compounds rarely exist in the gaseous state. c. Carbon sinks include forests and oceans. d. The carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is reduced by cutting trees. e. Carbon is concentrated in igneous rocks. 20. Which of the following is used to reduce SO2 emissions from coal-burning power plants? a. b. c. d. e. APES Catalytic converters Ultrafine mechanical filters Electrostatic precipitators Wet-scrubber units Afterburners Pg. 3 21. Global climate change occurs because increasing concentrations of greenhouse gasses in a. b. c. d. e. the troposphere absorb outgoing IR radiation the stratosphere absorb outgoing IR radiation the troposphere absorb incoming UV radiation the stratosphere absorb incoming UV radiation neither the troposphere nor the stratosphere absorb incoming UV radiation 22. Which of the following human activities is most closely associated with depletion of the stratospheric ozone layer? a. b. c. d. e. Mining of coal Disposal of refrigerators and air conditioners Heating of homes and factories Generation of electricity Agricultural irrigation 23. Although levels of CFCs in the atmosphere are much lower than those of CO2, CFCs are still potent greenhouse gases because they a. remain in the atmosphere for only a brief time b. lack natural sources c. are much more efficient at absorbing thermal radiation d. circulate through the troposphere more easily than CO2 does e. are more difficult to remove from smokestacks and tailpipes 24. Which of the following shows the approximate concentration of CO 2, N2, and O2 in dry air? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) CO2 78% 43% 36% 10% <1% N2 < 1% <1% 8% 70% 78% O2 21% 56% 56% 20% 21% 25. The atmosphere concentration of carbon dioxide increased from 278 ppm in 1790 to 383 ppm in 2007. What is the approximate percent increase in carbon dioxide concentration from 1790 to 2007? a. 38% b. 50% c. 92% d. 105% e. 138% 26. Of the following cities, which regularly experiences the worst levels of photochemical smog that is enhanced by thermal inversions? a. New York City, New York b. Los Angeles, California c. Portland, Oregon d. Atlanta, Georgia e. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 27. Possible effects of a warmer atmosphere include which of the following? i. Expanded ranges of tropical diseases ii. More intense hurricanes and typhoons iii. Increased crop damage from pests and diseases a. i only b. ii only c. i and iii only d. ii and iii only e. i, ii, and iii APES Pg. 4 28. Important factors that contribute to smog formation in the Los Angeles basin include which of the following? i. Ample summer sunshine ii. Sea-level elevation iii. High concentration of automobiles a. b. c. d. e. I only III only I and III only II and III only I, II and III 29. Which of the following is an appropriate remediation strategy for removing radon gas from the home? a. b. c. d. e. Use filtered water for drinking and bathing. Do not occupy the basement of the home. Place monitors in suspect areas of the home. Remove and replace soil in crawl spaces under the home. Seal or ventilate places where radon enters the living space. 30. Which of the following is true of the Clean Air Act? a. b. c. d. e. It was passed by Congress during the early 1950s. It regulates the amount of CO2 emitted by power plants. It has remained largely unmodified since it was originally signed into law. It established a cap-and-trade program for SO2 in 1990. It is set to expire in 2015. 31. When a rainforest is slashed and burned, the local concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases. This is primarily due to a. Changes in the local climate b. Oxidation of carbon compounds c. Cellular respiration of rain-forest plants d. Erosion of exposed soil e. Carbon dioxide being released by anaerobic organisms 32. Particulates can be removed from smokestack emissions by which of the following methods? a. b. c. d. e. Irradiation by UV light Electrostatic precipitators Catalytic converters Liquid chromatography Exhaust-stream aeration 33. Which of the following is a greenhouse gas that is produced by domestic livestock? a. b. c. d. e. NO2 CH4 O3 CO SO2 34. Which of the following are direct products of the use of hydrocarbon fuels in automobile engines? a. b. c. d. e. APES O, N and CO CO, Ar, and O3 CO2, H2O and O3 CO2, O3, and Pb CO2, NOx and VOCs Pg. 5 35. Which of the following has most directly resulted in increased skin cancer rates in Australia? a. b. c. d. e. Water pollution in the Antarctic Ocean Ozone depletion in the stratosphere Increased immigration of Asian people into Australia The occurrence of a solar maximum Global warming in the lower atmosphere 36. Which of the following is part of a positive feedback mechanism associated with global climate change? a. b. c. d. e. Increased gas mileage in cars Increased cloudiness caused by more moisture in the atmosphere Melting of Arctic sea ice Increased acidity of seawater Increased growth of CO2-absorbing trees and grasses 37. The three main anthropogenic sources of gaseous air pollutants in the United States are a. b. c. d. e. Soil erosion, volcanoes, and forest fires Soil erosion, volcanoes, and energy production Industry, construction, and agriculture Industry, transportation, and energy production Industry, transportation, and agriculture 38. Which of the following factors is fundamentally responsible for seasons on Earth? a. b. c. d. e. The varying distance of Earth from the Sun The tilt of Earth’s axis of rotation The latitudinal variation in temperature and precipitation The tidal pull of the Sun and Moon The anthropogenic greenhouse effect 39. The polar regions radiate away more heat energy than they receive from the Sun in the course of a year. However, they are prevented from becoming progressively colder each year primarily by the a. absorption of ultraviolet radiation by snow b. transport of heat through the atmosphere and oceans c. concentration of Earth’s magnetic field lines at the poles d. release of latent heat to the atmosphere when the polar ice caps melt e. generation of heat by glacial movement 40. Ozone in the stratosphere is most important to life at Earth’s surface because it absorbs a. b. c. d. e. gamma rays microwaves ultraviolet light visible light x-rays 41. Which of the following actions would reduce global greenhouse emissions? a. b. c. d. e. APES Increasing the use of automobiles Decreasing the number of nuclear power plants Replacing coal-burning power plants with wind farms Converting tropical forests to rice paddies Switching from hydroelectric power generation to power generation using natural gas as the primary fuel Pg. 6 42. The major source of radon in houses in the United States is a. b. c. d. e. furniture and carpets the underlying bedrock the troposphere nuclear power plants fossil-fuel combustion 43. Which of the following is a greenhouse gas that is also a by-product of anaerobic respiration? a. b. c. d. e. Methane, CH4 Nitrogen, N2 Oxygen, O2 Nitrogen dioxide, NO2 Hydrogen sulfide, H2S 44. Which of the following will occur if the trend of global temperature increase continues? a. b. c. d. e. Night temperatures will decrease as day temperatures increase. Tropical areas will become cooler than they currently are. Sea levels will drop due to increased evaporation. The incidence of insect-borne diseases will decrease. The troposphere will contain more water vapor. 45. The major human health problem related to radon accumulation is a. b. c. d. e. lung cancer heart disease pancreatic cancer cataracts malignant melanoma 46. Stratospheric ozone depletion is most likely to result in which of the following? a. b. c. d. e. Increased growth of food crops due to increasing amounts of ultraviolet radiation Extended grazing season for cattle Disruption of photosynthesis in plants Increased movement of the human population toward equatorial regions A higher percentage of cloudless days 47. Which of the following is a process that indirectly removes carbon from Earth’s atmosphere? a. b. c. d. e. Formation of carbonate deposits Outgassing by volcanoes Respiration by mammals Respiration by anaerobic bacteria Photodissociation by ultraviolet light 48. Many scientists maintain that a rise in sea level has occurred in the last hundred years as a result of global warming. If this is true, which of the following factors best explains such a rise? a. Increased precipitation b. Increased cloud cover c. Increased evapotranspiration d. Thermal expansion of the ocean e. Melting of permafrost APES Pg. 7 49. Which of the following natural events would most likely contribute to the cooling of Earth’s atmosphere? a. b. c. d. e. Earthquake Volcanism Hurricane Tsunami Monsoon 50. One solution for reducing the amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide would be to a. b. c. d. e. increase oceanic temperatures to enhance carbon dioxide uptake increase the rate of removal of tropical rain forests decrease the total area of rice paddies decrease the use of fossil fuels decrease the production of chlorfluorocarbons 51. The drop in stratospheric ozone levels in the Southern Hemisphere (the “ozone hole”) is most evident during which season? a. Antarctic spring (October) b. Antarctic autumn (April) c. Antarctic summer only (January) d. Antarctic winter only (July) e. Both Antarctic summer and Antarctic winter (January and July) 52. If Earth had no atmosphere, the mean surface temperature would be approximately -15C. With our present atmosphere, Earth’s mean surface temperature is approximately +15C. Which of the following is the best explanation for this difference? a. Reflection of incident solar radiation by clouds b. Scattering of visible radiation by aerosols c. Absorption of ultraviolet radiation by the ozone layer d. Absorption of infrared radiation by atmospheric gases e. The breakdown of oxygen molecules in the thermosphere 53. Which of the following would be the strongest evidence in support of a scientist’s contention that a local area was experiencing acid deposition? a. A sudden die-off of all the fish in a local stream b. A gradual increase in the temperature of a local lake c. An increase in the rate of photosynthesis of aquatic plants in a local lake d. A long-term increase in the pH of a local pond e. An increase in the concentration of soluble heavy metals in a local pond 54. If mean global temperature keeps on increasing as predicted by contemporary scientists, which of the following is most likely? a. There will be fewer insect pests and disease-carrying organisms. b. Specialist species living in fragile ecosystems will risk extinction. c. There will be an increase in sulfate concentrations in wetlands. d. There will be an increase in the reproductive rate of mammals. e. The geographical range of many plants will move toward the equator. 55. During an El-Nino- Southern Oscillation event, which of the following best describes conditions in the eastern part of the tropical Pacific Ocean (e.g., near Peru and Ecuador)? APES Sea Surface Temperature Rainfall (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Low High Low High Normal Low Low High High High Pg. 8 56. True statements about ozone include which of the following? a. b. c. d. e. i. It is a pollutant in the troposphere ii. It filters out most of the UVC radiation in the stratosphere iii. Most of it is formed in the stratosphere by reaction between carbon dioxide and free oxygen atoms. i only ii only iii only i and ii only i, ii, and iii 57. Which of the following best explains why it is predicted that ozone depletion over the poles will be at its worst between 2010 and 2019? a. Projected global warming from carbon dioxide emissions is expected to reach a peak during those years. b. Ozone-depleting chemical produced before their use was banned will take that long to reach peak concentrations in the stratosphere. c. Deforestation in tropical regions is expected to reach a peak during the second decade of the twentyfirst century. d. Increased global population will lead to an increase in per capita CO 2 production. e. Acid deposition will continue to increase, reaching a peak in approximately 2015. 58. Smoke from forest fires is most likely to affect air quality over larger areas for many days when a. b. c. d. e. Smog is produced due to chemical reactions in the atmosphere A persistent atmospheric inversion exists in the region Oak trees are burned, releasing terpenes into the atmosphere Primary, rather than secondary, forests are burned Vegetation in the region is green and burns more slowly 59. Global warming is most likely to directly cause which of the following? a. b. c. d. e. Shifting of grain belts toward the equator Falling sea levels in the Southern Hemisphere Coastal flooding and submersion of low-lying areas A decrease in the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere An increase in the number and size of glaciers 60. Which of the following is an important contributor to both global warming and ozone depletion? a. b. c. d. e. APES An increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide to higher-than-preindustrial levels A buildup of methane in the stratosphere to higher-than-preindustrial levels An increase in the levels of ultraviolet radiation reaching Earth’s surface An increase in the amount of infrared solar radiation absorbed in the troposphere A release of chlorofluorocarbons to the atmosphere Pg. 9 Key AP Environmental Science Air Pollution, Climate Change, & Ozone Depletion Unit Test Name: _________________________________________________ SID# ________ Questions 1-3 refer to the following regions of Earth’s atmosphere. (a) Thermosphere (b) Exosphere (c) Troposhpere (d) Mesosphere (e) Stratosphere 1. The phenomenon causing global warming occurs primarily in this region of the atmosphere. C 2. The beneficial ozone layer is in this region of the atmosphere. E 3. Most oxygen is found in this layer of the atmosphere. C Questions 4-6 refer to the gases listed below. A. B. c. d. e. H2O CO2 CH4 O3 CCl2F2 4. A greenhouse gas that is exclusively anthropogenic ____E____ 5. The most abundant nonanthropogenic greenhouse gas ____A____ 6. A greenhouse gas that, in the lower troposphere, is formed by photochemical reactions ___D_____ Questions 7-8 refer to the following air pollutants. A Sulfur dioxide B Lead C Ozone D Hydrocarbons E Particulates 7. Most often cited as the causative factor for acid deposition ___A_____ 8. Considered harmful in the troposphere but beneficial in the stratosphere APES ___C_____ Pg. 1 Questions 9-12 refer to the layers of Earth’s atmosphere in the temperature profile shown below. 9. Region where the protective ozone layer is located ___B_____ 10. Region that contains the majority of molecules in the atmosphere ___A_____ 11. Region largely responsible for the weather experienced at the Earth’s surface 12. Region with the lowest atmospheric pressure ____A____ ___E_____ Questions 13-16 refer to the substances listed. a. Asbestos b. Radon c. Lead d. Carbon monoxide e. Formaldehyde 13. Found in old plumbing pipes and fixtures and some ceramic glazes __C_____ 14. Composed of fibers known to cause lung disease _____A____ 15. Emitted from most manufactured building materials and furniture _____E_____ 16. Colorless, odorless gas that is naturally occurring decay product of uranium ____B______ APES Pg. 2 Questions 17-18 refer to the following graph. 17. The data in the graph can be useful in explaining the greenhouse effect when they are compared with a. volcanic activity b. sunspot activity c. mean global temperatures d. annual nitrous oxide production e. cycles of flooding and drought 18. The annual fluctuation in carbon dioxide concentration can best be explained by the a. seasonal use of fossil fuels b. regularity of volcanic activity c. deforestation in the tropics d. El Nino events e. seasonal photosynthetic activity of green plants 19. Which of the following is true of carbon as it cycles in nature? a. Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis. b. Carbon compounds rarely exist in the gaseous state. c. Carbon sinks include forests and oceans. d. The carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is reduced by cutting trees. e. Carbon is concentrated in igneous rocks. APES Pg. 3 20. Which of the following is used to reduce SO2 emissions from coal-burning power plants? a. Catalytic converters b. Ultrafine mechanical filters c. Electrostatic precipitators d. Wet-scrubber units e. Afterburners 21. Global climate change occurs because increasing concentrations of greenhouse gasses in a. the troposphere absorb outgoing IR radiation b. the stratosphere absorb outgoing IR radiation c. the troposphere absorb incoming UV radiation d. the stratosphere absorb incoming UV radiation e. neither the troposphere nor the stratosphere absorb incoming UV radiation 22. Which of the following human activities is most closely associated with depletion of the stratospheric ozone layer? a. Mining of coal b. Disposal of refrigerators and air conditioners c. Heating of homes and factories d. Generation of electricity e. Agricultural irrigation 23. Although levels of CFCs in the atmosphere are much lower than those of CO2, CFCs are still potent greenhouse gases because they a. remain in the atmosphere for only a brief time b. lack natural sources c. are much more efficient at absorbing thermal radiation d. circulate through the troposphere more easily than CO 2 does e. are more difficult to remove from smokestacks and tailpipes 24. Which of the following shows the approximate concentration of CO2, N2, and O2 in dry air? CO2 N2 O2 a. 78% < 1% 21% b. 43% <1% 56% c. 36% 8% 56% d. 10% 70% 20% e. <1% 78% 21% 25. The atmosphere concentration of carbon dioxide increased from 278 ppm in 1790 to 383 ppm in 2007. What is the approximate percent increase in carbon dioxide concentration from 1790 to 2007? a. 38% b. 50% c. 92% d. 105% e. 138% 26. Of the following cities, which regularly experiences the worst levels of photochemical smog that is enhanced by thermal inversions? a. New York City, New York b. Los Angeles, California c. Portland, Oregon d. Atlanta, Georgia e. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania APES Pg. 4 27. Possible effects of a warmer atmosphere include which of the following? i. Expanded ranges of tropical diseases ii. More intense hurricanes and typhoons iii. Increased crop damage from pests and diseases a. i only b. ii only c. I and iii only d. ii and iii only e. I, ii, and iii 28. Important factors that contribute to smog formation in the Los Angeles basin include which of the following? i.Ample summer sunshine ii.Sea-level elevation iii.High concentration of automobiles a. b. c. d. e. I only III only I and III only II and III only I, II and III 29. Which of the following is an appropriate remediation strategy for removing radon gas from the home? a. Use filtered water for drinking and bathing. b. Do not occupy the basement of the home. c. Place monitors in suspect areas of the home. d. Remove and replace soil in crawl spaces under the home. e. Seal or ventilate places where radon enters the living space. 30. Which of the following is true of the Clean Air Act? a. It was passed by Congress during the early 1950s. b. It regulates the amount of CO2 emitted by power plants. c. It has remained largely unmodified since it was originally signed into law. d. It established a cap-and-trade program for SO2 in 1990. e. It is set to expire in 2015. 31. When a rainforest is slashed and burned, the local concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases. This is primarily due to a. Changes in the local climate b. Oxidation of carbon compounds c. Cellular respiration of rain-forest plants d. Erosion of exposed soil e. Carbon dioxide being released by anaerobic organisms 32. Particulates can be removed from smokestack emissions by which of the following methods? a. Irradiation by UV light b. Electrostatic precipitators c. Catalytic converters d. Liquid chromatography e. Exhaust-stream aeration 33. Which of the following is a greenhouse gas that is produced by domestic livestock? a. NO2 b. CH4 c. O3 d. CO e. SO2 APES Pg. 5 34. Which of the following are direct products of the use of hydrocarbon fuels in automobile engines? a. O, N and CO b. CO, Ar, and O3 c. CO2, H2O and O3 d. CO2, O3, and Pb e. CO2, NOx and VOCs 35. Which of the following has most directly resulted in increased skin cancer rates in Australia? a. Water pollution in the Antarctic Ocean b. Ozone depletion in the stratosphere c. Increased immigration of Asian people into Australia d. The occurrence of a solar maximum e. Global warming in the lower atmosphere 36. Which of the following is part of a positive feedback mechanism associated with global climate change? a. Increased gas mileage in cars b. Increased cloudiness caused by more moisture in the atmosphere c. Melting of Arctic sea ice d. Increased acidity of seawater e. Increased growth of CO2-absorbing trees and grasses 37. The three main anthropogenic sources of gaseous air pollutants in the United States are a. Soil erosion, volcanoes, and forest fires b. Soil erosion, volcanoes, and energy production c. Industry, construction, and agriculture d. Industry, transportation, and energy production e. Industry, transportation, and agriculture 38. Which of the following factors is fundamentally responsible for seasons on Earth? a. The varying distance of Earth from the Sun b. The tilt of Earth’s axis of rotation c. The latitudinal variation in temperature and precipitation d. The tidal pull of the Sun and Moon e. The anthropogenic greenhouse effect 39. The polar regions radiate away more heat energy than they receive from the Sun in the course of a year. However, they are prevented from becoming progressively colder each year primarily by the a. absorption of ultraviolet radiation by snow b. transport of heat through the atmosphere and oceans c. concentration of Earth’s magnetic field lines at the poles d. release of latent heat to the atmosphere when the polar ice caps melt e. generation of heat by glacial movement 40. Ozone in the stratosphere is most important to life at Earth’s surface because it absorbs a. gamma rays b. microwaves c. ultraviolet light d. visible light e. x-rays APES Pg. 6 41. Which of the following actions would reduce global greenhouse emissions? a. Increasing the use of automobiles b. Decreasing the number of nuclear power plants c. Replacing coal-burning power plants with wind farms d. Converting tropical forests to rice paddies e. Switching from hydroelectric power generation to power generation using natural gas as the primary fuel 42. The major source of radon in houses in the United States is a. furniture and carpets b. the underlying bedrock c. the troposphere d. nuclear power plants e. fossil-fuel combustion 43. Which of the following is a greenhouse gas that is also a by-product of anaerobic respiration? a. Methane, CH4 b. Nitrogen, N2 c. Oxygen, O2 d. Nitrogen dioxide, NO2 e. Hydrogen sulfide, H2S 44. Which of the following will occur if the trend of global temperature increase continues? a. Night temperatures will decrease as day temperatures increase. b. Tropical areas will become cooler than they currently are. c. Sea levels will drop due to increased evaporation. d. The incidence of insect-borne diseases will decrease. e. The troposphere will contain more water vapor. 45. The major human health problem related to radon accumulation is a. lung cancer b. heart disease c. pancreatic cancer d. cataracts e. malignant melanoma 46. Stratospheric ozone depletion is most likely to result in which of the following? a. Increased growth of food crops due to increasing amounts of ultraviolet radiation b. Extended grazing season for cattle c. Disruption of photosynthesis in plants d. Increased movement of the human population toward equatorial regions e. A higher percentage of cloudless days 47. Which of the following is a process that indirectly removes carbon from Earth’s atmosphere? a. Formation of carbonate deposits b. Outgassing by volcanoes c. Respiration by mammals d. Respiration by anaerobic bacteria e. Photodissociation by ultraviolet light APES Pg. 7 48. Many scientists maintain that a rise in sea level has occurred in the last hundred years as a result of global warming. If this is true, which of the following factors best explains such a rise? a. Increased precipitation b. Increased cloud cover c. Increased evapotranspiration d. Thermal expansion of the ocean e. Melting of permafrost 49. Which of the following natural events would most likely contribute to the cooling of Earth’s atmosphere? a. Earthquake b. Volcanism c. Hurricane d. Tsunami e. Monsoon 50. One solution for reducing the amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide would be to a. increase oceanic temperatures to enhance carbon dioxide uptake b. increase the rate of removal of tropical rain forests c. decrease the total area of rice paddies d. decrease the use of fossil fuels e. decrease the production of chlorfluorocarbons 51. The drop in stratospheric ozone levels in the Southern Hemisphere (the “ozone hole”) is most evident during which season? a. Antarctic spring (October) b. Antarctic autumn (April) c. Antarctic summer only (January) d. Antarctic winter only (July) e. Both Antarctic summer and Antarctic winter (January and July) 52. If Earth had no atmosphere, the mean surface temperature would be approximately -15C. With our present atmosphere, Earth’s mean surface temperature is approximately +15C. Which of the following is the best explanation for this difference? a. Reflection of incident solar radiation by clouds b. Scattering of visible radiation by aerosols c. Absorption of ultraviolet radiation by the ozone layer d. Absorption of infrared radiation by atmospheric gases e. The breakdown of oxygen molecules in the thermosphere 53. Which of the following would be the strongest evidence in support of a scientist’s contention that a local area was experiencing acid deposition? a. A sudden die-off of all the fish in a local stream b. A gradual increase in the temperature of a local lake c. An increase in the rate of photosynthesis of aquatic plants in a local lake d. A long-term increase in the pH of a local pond e. An increase in the concentration of soluble heavy metals in a local pond 54. If mean global temperature keeps on increasing as predicted by contemporary scientists, which of the following is most likely? a. There will be fewer insect pests and disease-carrying organisms. b. Specialist species living in fragile ecosystems will risk extinction. c. There will be an increase in sulfate concentrations in wetlands. d. There will be an increase in the reproductive rate of mammals. e. The geographical range of many plants will move toward the equator. APES Pg. 8 55. During an El-Nino- Southern Oscillation event, which of the following best describes conditions in the eastern part of the tropical Pacific Ocean (e.g., near Peru and Ecuador)? Sea Surface Temperature a. b. c. d. e. Low Low High High High Rainfall Low High Low High Normal 56. True statements about ozone include which of the following? i. It is a pollutant in the troposphere ii. It filters out most of the UVC radiation in the stratosphere iii. Most of it is formed in the stratosphere by reaction between carbon dioxide and free oxygen atoms. a. i only b. ii only c. iii only d. i and ii only e. i, ii, and iii 57. Which of the following best explains why it is predicted that ozone depletion over the poles will be at its worst between 2010 and 2019? a. Projected global warming from carbon dioxide emissions is expected to reach a peak during those years. b. Ozone-depleting chemical produced before their use was banned will take that long to reach peak concentrations in the stratosphere. c. Deforestation in tropical regions is expected to reach a peak during the second decade of the twentyfirst century. d. Increased global population will lead to an increase in per capita CO 2 production. e. Acid deposition will continue to increase, reaching a peak in approximately 2015. 58. Smoke from forest fires is most likely to affect air quality over larger areas for many days when a. Smog is produced due to chemical reactions in the atmosphere b. A persistent atmospheric inversion exists in the region c. Oak trees are burned, releasing terpenes into the atmosphere d. Primary, rather than secondary, forests are burned e. Vegetation in the region is green and burns more slowly 59. Global warming is most likely to directly cause which of the following? a. Shifting of grain belts toward the equator b. Falling sea levels in the Southern Hemisphere c. Coastal flooding and submersion of low-lying areas d. A decrease in the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere e. An increase in the number and size of glaciers 60. Which of the following is an important contributor to both global warming and ozone depletion? a. An increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide to higher-than-preindustrial levels b. A buildup of methane in the stratosphere to higher-than-preindustrial levels c. An increase in the levels of ultraviolet radiation reaching Earth’s surface d. An increase in the amount of infrared solar radiation absorbed in the troposphere e. A release of chlorofluorocarbons to the atmosphere APES Pg. 9