Glossary for the Atmosphere
advertisement
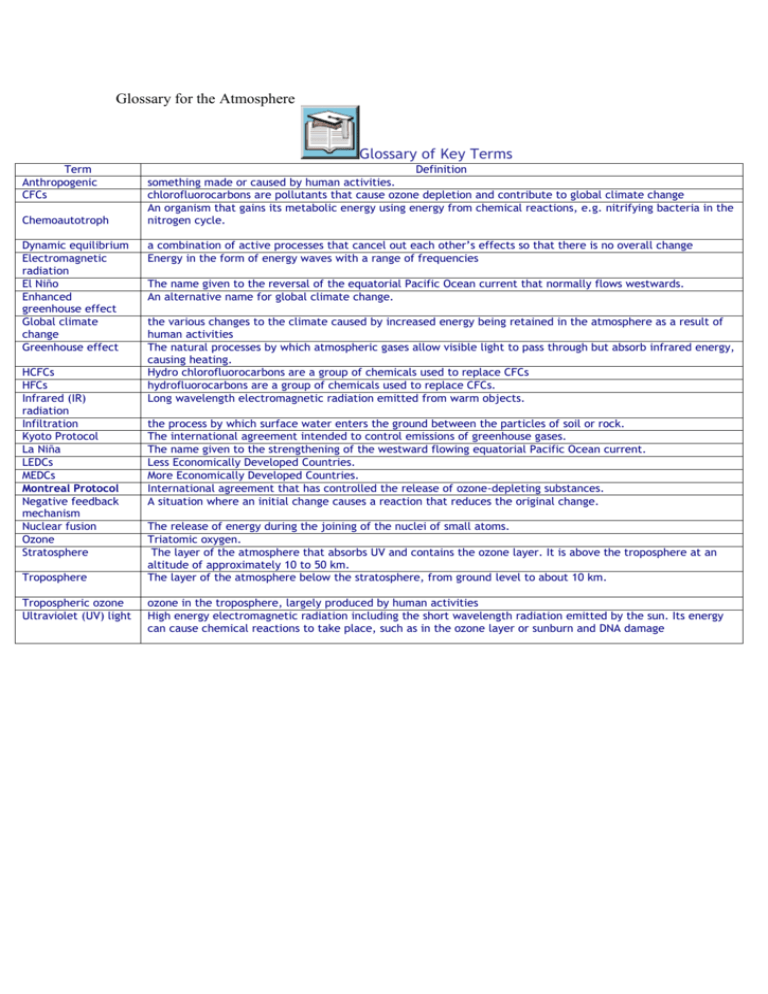
Glossary for the Atmosphere Glossary of Key Terms Term Anthropogenic CFCs Chemoautotroph Dynamic equilibrium Electromagnetic radiation El Niño Enhanced greenhouse effect Global climate change Greenhouse effect HCFCs HFCs Infrared (IR) radiation Infiltration Kyoto Protocol La Niña LEDCs MEDCs Montreal Protocol Negative feedback mechanism Nuclear fusion Ozone Stratosphere Troposphere Tropospheric ozone Ultraviolet (UV) light Definition something made or caused by human activities. chlorofluorocarbons are pollutants that cause ozone depletion and contribute to global climate change An organism that gains its metabolic energy using energy from chemical reactions, e.g. nitrifying bacteria in the nitrogen cycle. a combination of active processes that cancel out each other’s effects so that there is no overall change Energy in the form of energy waves with a range of frequencies The name given to the reversal of the equatorial Pacific Ocean current that normally flows westwards. An alternative name for global climate change. the various changes to the climate caused by increased energy being retained in the atmosphere as a result of human activities The natural processes by which atmospheric gases allow visible light to pass through but absorb infrared energy, causing heating. Hydro chlorofluorocarbons are a group of chemicals used to replace CFCs hydrofluorocarbons are a group of chemicals used to replace CFCs. Long wavelength electromagnetic radiation emitted from warm objects. the process by which surface water enters the ground between the particles of soil or rock. The international agreement intended to control emissions of greenhouse gases. The name given to the strengthening of the westward flowing equatorial Pacific Ocean current. Less Economically Developed Countries. More Economically Developed Countries. International agreement that has controlled the release of ozone-depleting substances. A situation where an initial change causes a reaction that reduces the original change. The release of energy during the joining of the nuclei of small atoms. Triatomic oxygen. The layer of the atmosphere that absorbs UV and contains the ozone layer. It is above the troposphere at an altitude of approximately 10 to 50 km. The layer of the atmosphere below the stratosphere, from ground level to about 10 km. ozone in the troposphere, largely produced by human activities High energy electromagnetic radiation including the short wavelength radiation emitted by the sun. Its energy can cause chemical reactions to take place, such as in the ozone layer or sunburn and DNA damage