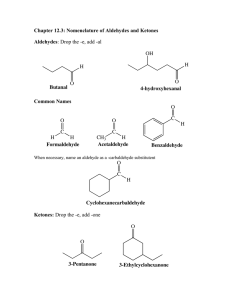
SECTION 18 ² ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION REACTIONS
advertisement

SECTION 18 ² ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION REACTIONS 18-1 -- Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones x Common Names of Aldehydes and Ketones x Substituents or ´Branchesµ x IUPAC Names of Aldehydes and Ketones 18-3 -- Strength of the Carbonyl Bond (C=O) 18-4 -- Spectroscopy of Aldehydes and Ketones x IR, 1H NMR, and 13C NMR 18-5 -- Nucleophilic Addition Reactions of the Carbonyl Group x 7 Reactions to be Examined in Detail x Why are Aldehydes More Reactive than Ketones? x Effect of Alkyl Groups (Branches) 18-6 -- The Hydration Reaction x Mechanism of Base-Catalyzed Hydration x Mechanism of Acid-Catalyzed Hydration 18-8 -- Formation of Acetals (2 Alkoxy Groups, -OR, on a Carbon) x Acid-Catalyzed Mechanism x Use of Acetals as Protecting Groups 18-11 -- Cyanohydrin Formation (-CN and -OH on a Carbon) x Can be Acid-Catalyzed or Base-Catalyzed x Mechanism of Cyanohydrin Formation 18-11 -- Hydride Reactions x Use of Lithium Aluminum Hydride, LiAlH4 (or ´LAHµ) x Use of Sodium Borohydride, NaBH4 18-12 -- Grignard Additions to the Carbonyl x Addition of R·-MgX to the Carbonyl (R2C=O) 18-12 -- Reactions of the Carbonyl (C=O) with Amines x Yields Different Products Depending on the Type of Amine (1° or 2°) x Mechanisms: Formations of Imines, Carbinolamines, and Enamines x Tautomerization is Observed 18-14 -- Imine Derivatives x Hydrazone, Semicarbazone, and Oxime 18-15 -- Reduction of Carbonyls to Methylene Groups (-CH2-) x Wolff-Kishner Reaction Requires Basic Conditions x Clemmenson Reduction (Zn/Hg in aqueous HCl) x Reduction of Thioacetals 18-16 -- The Wittig Reaction www.OChemNotes.com x Phosphonium Ylides (´The Wittig Reagentµ) x Mechanism of Ylide Preparation x Why is the Reaction not Stereospecific? 18-18 -- Oxidation of Aldehydes x Oxidation Using Chromium Reagents (PCC, H2CrO4, Jones Reagent, etc«) x Oxidation Using the Tollens Reagent 18-19 -- Preparation of Aldehydes x Via Ozonolysis of Alkenes x Via Hydroboration of Terminal Alkynes (HCƱCR) x Via Oxidation of Alcohols Using PCC x Via the Use of Mild Reducting Agents (´:H-´) 18-20 -- Preparation of Ketones x Via Ozonolysis of Alkenes x Via Friedel-Crafts Acylation (AlCl3 as Catalyst) x Via Alkyne Hydration x Via Oxidation of Alcohols Using PCC or H2CrO4 x Via Addition of ´:R-´ to Acid Chlorides 18-21 -- Conjugate Additions of Nucleophiles to Ĵ,ǀ-Unsaturated Carbonyls x ´Michael Additionµ x Resonance-Stabilized Enolate Ion x Protonation and Tautomerization 18-22 -- Some Nucleophiles Add Directly to the Carbonyl Carbon x Less Basic Nucleophiles vs. Strongly Basic Nucleophiles x Kinetic vs. Thermodynamic Control x Resonance-Stabilization of the Negative (-1) Charge www.OChemNotes.com SECTION 18 – ALDEHYDES and KETONES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION REACTIONS Were the FREE Section 18 Notes Useful? Want the FULL VERSION of the Section 18 Notes? Download Them Instantly for Only $6.99 at: OChemNotes.com www.OChemNotes.com