Chapter 17 (Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition to the
advertisement

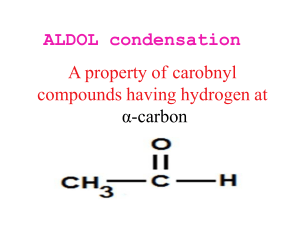
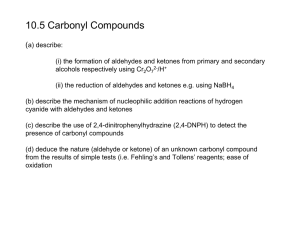
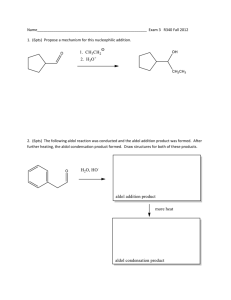
Chapter 17 (Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group) Nomenclature Nucleophilic vs. Electrophilic attack Alkyl groups stabilize reactants (electronic) and crowd product (steric) Table 17.3 Equilibrium Constants and Relative Rates of Hydration Synthetic Strategy 1. Protect C=O 2. Alkylate 3. Restore C=O Stereospecificity of carbonyl additions (slide 40) Chapter 18 (Enols and Enolates) Greek letter assignments Acidity of α-Hydrogen Table 18.1 pKa Values of Some Aldehydes and Ketones Intramolecular aldol condensation Mixed aldol condensations (will be on test) To carry out a mixed aldol condensation: 1. Choose component that cannot form an enolate (slide 24) 2. OR use a very strong/non-nucleophilic base (slide 25) Enolization Enol Stability (slides 29-30) Stereochemistry (slides 34-36) Conjugation (slides 37-44) 1,2-addition Strongly basic nucleophiles: Grignard reagents, LiAlH4, NaBH4, sodium acetylide strongly basic nucleophiles add irreversibly 1,4-addition Weakly basic nucleophiles: cyanide ion (CN-), thiolate ions (RS-), ammonia and amines, azide ion (N3-) weakly basic nucleophiles add reversibly