Plant Systems
advertisement

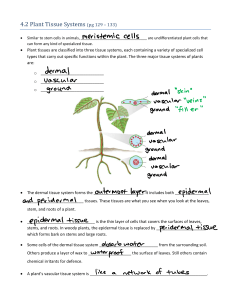
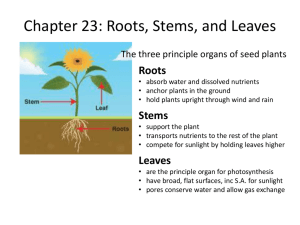
Plant Systems Plant Systems There are two distinguishing features of plants: 1. Green in colour – caused by chlorophyll 2. Have structures (usually roots) to anchor them in place Plants make their own food by photosynthesis This means they do not need to move around in search of food They also do not need complicated organ systems found in animals Plant Systems Plants do need to perform many of the same functions as animals: exchange gases with their surroundings an internal transportation system to move water and nutrients around their body to reproduce Plant Systems The plant is divided into two main “body systems”: Plant Systems The plant is divided into two main “body systems”: Plant Systems 1. Root System Below ground Anchors plant Made up of one or more separate roots Can spread underground to a very large area Absorbs water and minerals from the soil (done by root hairs) Stores food Plant Systems 2. Shoot system Above ground Two main functions: a) Photosynthesis (for food) b) To produce flowers (for reproduction) Made up of the leaf, flower, and stem Plant Systems 2. Shoot system a) The Leaf Main photosynthetic structure of plant Photosynthesis is done by the chloroplast Chloroplasts contain flat, disc-like structures called thylakoids Thylakoids are arranged in stacks called grana Grana act as solar collectors Gases enter the leaf through the stomata Have a waxy layer called a cuticle that protects the leaf from drying out Plant Systems 2. Shoot system b) The Flower Used for sexual reproduction – there are male and female parts Reproduction occurs by pollination Seeds are formed, which are stored in a fruit Plant Systems 2. Shoot system c) The Stem Supports branches, leaves, and flowers and provides a way to transport materials Transports materials by vascular tissues Plant Tissue Systems Plant Tissue Systems cells start as Meristematic Cells – undifferentiated plant cells that can divide and differentiate to form specialized cells (“plant” stem cells). Plant Found near the tips of roots/stems Plants have three tissue systems: dermal, vascular, and ground Plant Tissue Systems 1. Dermal Tissue System (skin) covers the entire outer surface of the plant – leaves, roots, stems, etc can be either: a) Epidermal tissue - a thin layer of cells covering the surface of leaves, stems, and roots b) Periderm tissue – in woody plants, it replaces the epidermal tissue by forming bark on stems and large roots Plant Tissue Systems 2. Vascular Tissue System (veins) found within every root, shoot, and leaf of the plant Is a transportation system: moves water, minerals, and other chemicals around the plant Two types: a) Xylem – made up of elongated cells that are not living - transports water and dissolved minerals upward from the roots b) Phloem - made up of elongated cells that are living – transports food materials and hormones throughout the plant (upward or downward) Plant Tissue Systems 3. Ground Tissue System (everything else) all other internal tissues in the root, stem, and leaves filter between the dermal and vascular tissues perform a variety of functions Plant Tissue Systems Plant Tissue Systems