Roots, Stems and Leaves
advertisement

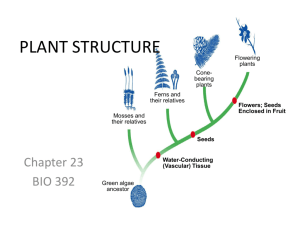
Roots, Stems and Leaves Chapter 23 Biology – Miller • Levine Specialized Tissue in Plants The three organs of a plant are the roots, stems and leaves The three tissue systems of a plant are dermal tissue, vascular tissue, and ground tissue A special type of tissue called meristematic tissue is the only plant tissue that can produce new cells by mitosis Found in the tips of shoots and roots Dermal Tissue The outer covering of a plant Consists of a single layer of epidermal cells Cuticle – a waxy layer that often covers the epidermis Provides protection against water loss & injury May include specialized structures such as root hairs and guard cells Vascular Tissue Transports water and nutrients throughout the plant Xylem – transports water; composed of dead cells Phloem – transports nutrients; composed of living cells called sieve tube elements Ground Tissue Lies between the dermal and vascular tissues Parenchyma – has thin cell walls and large central vacuoles Collenchyma – has strong, flexible cell walls and is found in larger plants Sclerenchyma – has extremely thick, rigid cells walls Roots Types of roots: Taproot - A thick primary root that grows long and is found mainly in dicots Fibrous roots – branch extensively and are found mainly in monocots Root Structure & Growth Root hairs – tiny projections from the epidermis that increases the surface area for absorption of water Cortex – layer of ground tissue Endodermis – layer of tissue that encloses the vascular tissue Root cap – protects the root as it forces its way through the soil Root Structure & Function Root Function Anchor a plant in the ground Absorb water and dissolved nutrients from the soil Stem Function & Types Three important functions: Produce leaves, branches and flowers Hold leaves up in the sunlight Transport substances between roots and leaves Two types: Monocot – has vascular bundles that contain the xylem & phloem scattered randomly Dicot – have vascular bundles organized in a ringlike pattern Monocots and Dicots Stem Structures Nodes – where leaves are attached Internodes – regions between the nodes Buds – contain undeveloped tissue that can produce new stems and leaves Leaf Structure Blade – thin, flattened section Petiole – thin stalk that attaches the leaf to the stem Veins – contain the xylem and phloem Leaf Structure Palisade mesophyll – tightly packed cells that absorb light Spongy mesophyll – loosely packed cells with air spaces Stomata – pore-like openings for taking in CO2 and releasing O2 Guard cells – cells that open and close the stomata Leaf Structure Leaf Functions Photosynthesis – takes place in the mesophyll cells of the leaf Transpiration – the loss of water from a plant through its leaves (helps to pull water up from the roots) Gas exchange – taking in carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen