Chapter Twenty One Vocabulary
advertisement

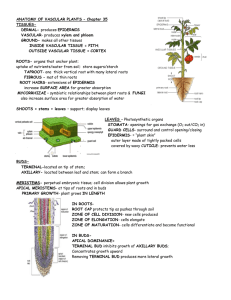
Chapter Twenty One Vocabulary 21.1 Parenchyma cell: cell with thin walls that forms tissues within leaves, roots, stems, and fruit of plants. Collenchyma cell: elongated cells with unevenly thick walls that form a supportive tissue of plants. Sclerenchyma cell: thick-walled, lignin-rich cells that form a supportive plant tissue. Dermal tissue: tissue system that covers the outside of plants and animals. Ground tissue: tissue system that makes up the majority of a plant. Vascular tissue: supportive and conductive tissue in plants, consisting of xylem and phloem. Xylem: tissue that transports water and dissolved minerals in vascular plants. Phloem: tissue that transports sugars in vascular plants. 21.2 Cohesion-tension theory: theory that explains how the physical properties of water allow it to move the xylem of plants. Transpiration: release of vapor through the pores of the skin or the stomata of plant tissue. Pressure-flow model: model for predicting how sugars are transported from photosynthetic tissue to the rest of a plant. 21.3 Vascular cylinder: center of a root or stem that contains xylem and phloem. Root hair: thin hair-like outgrowth of an epidermal cell of a plant root that absorbs water and minerals from the soil. Root cap: mass of cells that covers and protects the tips of plant roots. Meristem: undifferentiated plant tissue from which new cells are formed. Fibrous root: root system made up of many threadlike members of more or less equal length. Taproot: main root of some plants, usually larger than other roots and growing straight down from a stem. Primary growth: growth in vascular plants resulting in elongation of the plant body. Secondary growth: growth in woody plants resulting in wider roots, branches, and stems. 21.4 Blade: broad part of a leaf where most of the photosynthesis of a plant takes place. Petiole: stalk that attaches a leaf blade to a stem. Mesophyll: photosynthetic tissue of a leaf, located between the upper and lower epidermis. Guard cell: one of a pair of cells that controls the opening and closing of a stoma in plant tissue.