Q4 Study Guide
advertisement

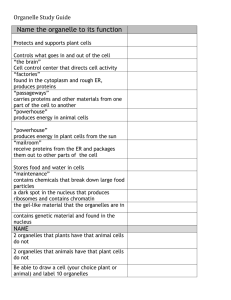
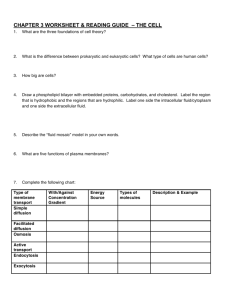
Name:____________________________________________ Date:________ Q4 Exam Study Guide. The exam is on Tuesday, May 26th. It will consist of 3540 multiple choice questions covering chapter 15 from the textbook and the chemistry handouts. Ch. 15….Cells, Organelles and Cell cycle Section 15.1. Microscope and cell theory 1. What would the total magnification be of a specimen being viewed with a 10x eyepiece lens and a 40x objective (nosepiece) lens? Total magnification = 10 x 40 = 400x 2. List the 3 parts of the cell theory. All living things are composed of cells. Cells make up the structure and function of livings. Cells are need to reproduce new cells. 3. Define the term resolution. What has better resolution, a light microscope or an electron microscope? Resolution is the ability to determine the difference between two closely spaced objects. Electron microscopes have better resolution than light microscopes. 4. List and explain the function of two cell parts found in plants that are not found in animal cells? Cell walls help support and protect the plant cells. Also, chloroplasts are in plants to make energy with photosynthesis. Section 15.2. Cell organelles and multicellular organization. Define the function of the following terms: 5. Cell membrane: The outer layer of all cells which controls the substances that pass in and out of the cell. 6. Nucleus: The control center of the cell and it contains the DNA. 7. Chloroplast: Organelle found only in plants that converts sunlight to energy. Organelle that converts food into energy that cells can use. 8. Mitochondria: Organelle that looks like a sac to store food and water. 9. Vacuole: Acts like a trash compactor and breaks down large food particles for the cell. 10. Lysosome: grain-shaped organelle that make proteins for the cell 11. Ribosomes: A watery-fluid that fills the spaces between organelles. 12. Cytoplasm: Organelle that receives proteins and then packages and ships to other places. 13. Golgi: A maze of passageways that helps make substances and carries proteins. 14. Endoplasmic Reticulum: 15. What name is given to a group of similar cells working together? Tissue 16. What does division of labor mean to an organism? Each different type of cell does a different job 17. What are the bones of the skull, fingers/toes, upper leg and breastbone called? Skull: Cranium Fingers/toes: Phalanges Breastbone: Sternum Upper leg: Femur; This is the biggest bone in the body. 18. Which of the following are the 4 biochemical compounds that living things require? A. Carbohydrates, Lysosomes, Mitochondria, Nucleus B. Cell walls, Vacuoles, Chloroplasts, Sunlight C. Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids D. None of these 19. What is the name for a group of proteins in living things that speed up chemical reactions? Enzymes 20. What are the levels of organization in living things? Cells Tissues Organ Organ System Organism Section 15.4 Reproduction of Cells 21. The main purpose of the cell cycle is to create new cells, how many cells would result from one cell going through 3 consecutive cell cycles? Hint. Memorize and use 2x where x=number of cell cycles. 2 3 = 2x2x2 = 8 cells 22. What is replication and in what stage of the cell cycle does it occur? Replication is the copying of DNA and it occurs in stage one of the cell cycle called interphase. 23. What is the main purpose of the stage of the cell cycle termed “mitosis”? In mitosis, the cell is rearranging the DNA and separating the copies of DNA so that each daughter cell gets an identical copy. Two new nucleii are formed in mitosis. 24. What happens in cytokinesis? In cytokinesis one cell splits (cytoplasm also splits ) into two cells, creating daughter cells. 25. Which stage of the cell cycle takes the longest? Interphase 26. What does epithelial tissue do? Epithelial tissue covers the surface of your body both inside and out. 27. If a cell needs one hour to complete the cell cycle, how many cells would result after 4 hours? 4 hours ÷ 1 hour = 4 cycles 2 4 = 16 cells 28. Which stage of the cell cycle takes the longest? Interphase 29. The cell membrane is made mostly of a double layer of molecules called A. Lipids B. proteins C. nucleic acids D. carbohydrates 30. What are hormones and what system of the body releases hormones as signals? Hormones are chemical signals for growth and development and they come out of glands in the endocrine system. 31. Bone and fat are considered which of the four types of tissue? Connective tissue Chemistry. Review all chemistry handouts. Know all 20 chemical symbols. 32. What the charge and location of an electron? Enraged Elliot Electron is negatively charged and located in shells outside the nucleus. 33. What is the charge and location of a proton? Perky Patty Proton is positively charged and found inside the nucleus. 34. What is the charge and location of a neutron? Nerdy Nelda Neutron is neutral (no charge) and is also found in the nucleus. 35. What does the term valence mean? The outer shell electrons which bind with other atoms (participate in chemical bonds) are called the valence electrons. These are the electrons with the highest energy. 36. What is the difference between a subscript and a coefficient? Subscript is a number written below and behind an element telling us the number and ratio of atoms. The coefficient is written in front of the chemical symbol but it tells the number of molecules. 37. Count the oxygen atoms in the chemical formula, 2Na2HPO4 Oxygen atoms: 2 x 4 = 8 total O’s 38. What are the reactants in the chemical equation, Na + Cl2 NaCl The reactants are the Na and the Cl2. 39. What is an ion? If an ion has 5 protons and 4 electrons, what is its overall charge? An ion is an atom with a positive or negative charge. The ion with 5 protons and 4 electrons has an overall charge of +1. 40. What does the law of conservation of mass (energy) say? This law means that in a chemical reaction, the overall quantity of mass or energy does not decrease or increase (cannot be created or destroyed). Its changed into a new form but stays the same.