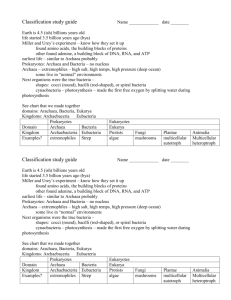
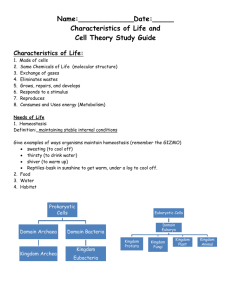
Taxonomy = a branch of biology that groups and names organisms
advertisement
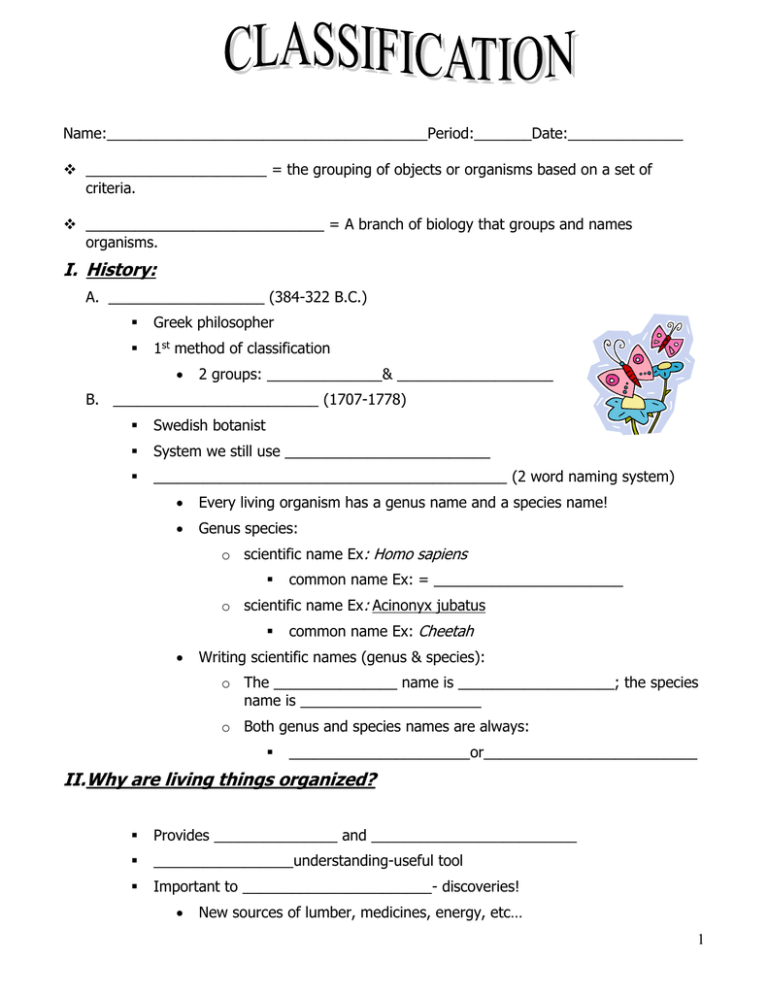
Name:_______________________________________Period:_______Date:______________ ______________________ = the grouping of objects or organisms based on a set of criteria. _____________________________ = A branch of biology that groups and names organisms. I. History: A. ___________________ (384-322 B.C.) Greek philosopher 1st method of classification 2 groups: ______________& ___________________ B. _________________________ (1707-1778) Swedish botanist System we still use _________________________ ___________________________________________ (2 word naming system) Every living organism has a genus name and a species name! Genus species: o scientific name Ex: Homo sapiens common name Ex: = _______________________ o scientific name Ex: Acinonyx jubatus common name Ex: Cheetah Writing scientific names (genus & species): o The _______________ name is ___________________; the species name is ______________________ o Both genus and species names are always: ______________________or__________________________ II.Why are living things organized? Provides _______________ and _________________________ _________________understanding-useful tool Important to _______________________- discoveries! New sources of lumber, medicines, energy, etc… 1 III. How are living things classified? A. _______________- series of categories, each one larger than the previous one ________________ (only one-least broad) ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________(Very Broad Category) B. Classified by similarities in: 1. _______________________ stages 2. __________________________analysis (DNA) 3. __________________________patterns IV. DOMAINS: Organisms are classified into ________________ according to cell type and structure Organisms are classified into ____________________ according to cell type, structure, and 2 Cell Types: nutrition 1) _____________________________________= have membrane-bound nucleus and organelles; usually more complex than prokaryotic cells 2) _____________________________________= does NOT have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles 3 Domains: 1) Bacteria 2) Archea (pronounced- ar KEE uh) 3) Eukarya A. _______________________ Prokaryotes Cell walls contain peptidoglycan (polymer of sugars) Contains Kingdom Bacteria B. _______________________ 2 More ancient than bacteria Prokaryotes Cell walls _________________ contain peptidoglycan Live in ___________________________ environments o Boiling hot springs, salty latkes, thermal vents on the oceans’ floors, mud of marshes where there is NO oxygen C. __________________________________ Eukaryotes Contains Kingdom Protists, Kingdom Fungi, Kingdom Plants, Kingdom Animals V. THE SIX KINGDOMS: 1. BACTERIA 2. ARCHAEA 3. PROTISTS 4. FUNGI 5. PLANTS 6. ANIMALS Flow Chart of Domains & Kingdoms: 3 Domains 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Bacteria Archaea Archaea Protists Plants Eukarya Fungi Animals 3 A. BACTERIA Cell type –_______________________ Cell walls with peptidoglycan Unicellular Autotroph (organism that makes their own heterotroph (organism that gets its feeding on other organisms) Common bacteria food) or nutrients by E. coli o Ex: bacteria you would find on your skin o Ex: streptococcus bacteria causes strep throat o Ex: __________________ B. ARCHAEA Cell type –_________________________ Cell walls ________________________contain peptidoglycan Unicellular Autotroph or heterotroph C. PROTISTS Paramecium Most _____________________ group Cell type – eukaryote Unicellular and multicellular Some ___________________, ___________________ and _________________ DO NOT have _____________________________ Usually live in ______________environments Ex: ___________________, slime mold, ___________________ Slime mold D. FUNGI Cell type – eukaryote Most multicellular ____________________________- absorb nutrients obtained by ________________________ dead organisms and wastes in environment Cell walls with chitin (polymer) Ex: ______________, _____________________ Kelp 4 E. PLANTS Cell type – eukaryote Multicellular ___________________________ (autotrophs) Most have _____________________ in their cell walls ________________________ organized into ____________ (roots, stems, leaves) F. ANIMALS Cell type – eukaryote Multicellular Consumers that _______ and digest ______________________________for food No ____________________________ Have tissues organized into complex organ systems Kingdom Characteristics Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Cell Type Cell Walls Number of Cells Nutrition Eukarya Protists Prokaryotic Contains peptidoglycan Does NOT contain peptidoglycan Unicellular Autotroph or heterotroph Fungi Plants Animals Cellulose NO Cell walls Eukaryotic Some with cellulose Chitin Unicellular & Multicellular Most Multicellular Heterotroph Multicellular Autotroph Heterotroph 5 Classification Practice In the exercises that follow, arrange the items listed into different groups. Give each group a title indicating what the members of that group have in common. 1. German Shepherd, Great Dane, parrot, Irish setter, canary, husky, robin, pigeon Title _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ Title ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ 2. Apples, peas, orange, banana, carrot, lettuce, turnip, pear, grape, potato Title _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ Title ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ 3. Steak, football, sausage, chair, table, bacon, sofa, baseball bat, cleats, ham, bookcase Title _________________ Title__________________ Title_________________ _________________ __________________ ________________ _________________ __________________ ________________ _________________ __________________ ________________ _________________ __________________ ________________ _____________________ _______________________ ____________________ 4. Number the following classification groups from the largest to the smallest (the largest group will be Number 1). Also, define each of the classification groups below. _____ Class _____ Genus _____ Kingdom _____ Species _____ Phylum _____ Order _____ Family 6 Cladogram Practice Step One “The Chart”: 1. First, you need to make a “characteristics chart” the helps you analyze which characteristics each species. Fill in a “x” for yes it has the trait and “o” for “no” for each of the organisms below. Backbone Legs Hair Earthworm Fish Lizard Human “yes count” Step Two “The Cladogram”: This step converts the above chart into a cladogram. The traits are written on the main line, and species go on the branches. On the cladogram below, try to put all the characters and the species in the correct evolutionary history. 2. Complete the following chart the same way as the above example. After you complete the chart, use it to create a cladogram on the back of this paper. Hair Legs Thumbs eyes Human Snake Monkey Mouse Starfish 7 Interpreting a Cladogram First, let’s practice interpreting some cladograms. Looking at the images, answer the questions below 1. Which animals have mammary glands? 2. What animal does not have jaws? 3. Which animals have lungs? 4. What other animals would come after the chimp? 5. What could the character trait be that would come after the chimp? 6. What character trait separates salamanders and lizards? 7. Based on the cladogram, which shared a common ancestor most recently: a mouse and a lizard, or a mouse and a perch? 8. Make a characteristics chart (hint: look at previous page for an example) 8