AP Biology Chapter 27 Quiz - mr-youssef-mci

AP Biology Chapter 27 Quiz
1.
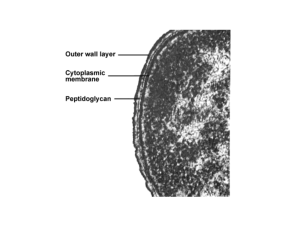
Which outer-membrane feature is specific to gram-positive bacteria? (C) a.
Peptidoglycan layer sandwiched between two plasma membranes. b.
The presence of membranous proteins. c.
A thick, outer layer of peptidoglycan. d.
A thick, inner layer of peptidoglycan. e.
No peptidoglycan.
2.
Which outer-membrane feature is specific to gram-negative bacteria? (C) a.
A thick, outer layer of peptidoglycan. b.
No peptidoglycan. c.
Presence of potentially toxic lippolysaccharides. d.
The presence of membranous proteins. e.
Its membrane complex is likely to trap CV-I complexes.
3.
What is a common purpose between capsules, pili and fimbriae? (D) a.
Reproduction b.
Motility c.
Transfer of DNA d.
Adherence e.
Attack
4.
What type of prokaryote can survive in an environment that is plentiful with inorganic chemicals, but has no light? (C) a.
Photoautotroph b.
Photoheterotroph c.
Chemoautotroph d.
Chemoheterotroph e.
Magical Bacteria
5.
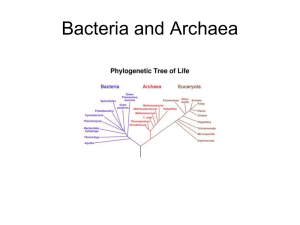
Which of the following characteristics is exhibited in archaea but not bacteria? (D) a.
Presence of peptidoglycan. b.
Circular chromosome c.
Linear chromosome d.
Methionine as the initiator amino acid e.
Membrane-enclosed organelles.
6.
Which type of archaea can survive in environments such as the Dead Sea and the Great Salt
Lake? (B) a.
Extreme thermophiles b.
Extreme halophiles c.
Methanogens d.
Decomposers e.
Parasites
7.
The E. Coli in our intestines had undergone a sporadic mutation. Rather than up taking the nutrients from our digestive tracks and producing Vitamin K, through an alternate chemical
AP Biology Chapter 27 Quiz
pathway, it now produces a lethal toxin. What type of relationship does the E. Coli now share with the host? (C) a.
Mutualism b.
Commensialism c.
Parasitism
8.
Following an initial prokaryotic infection, the patient suddenly becomes lethally ill after a small dose of anti-biotics. What possible type of prokaryote might have caused this infection? (E) a.
Gram-positive bacteria b.
Extremely halophilic archaea c.
Methanogen d.
Chlamydias e.
Gram-negative bacteria
9.
Of these following choices, which has the closest similarities to eukaryotes in terms of DNA and cellular structures? (D) a.
Gram positive bacteria b.
Gram negative bacteria c.
Spirochetes d.
Archaea e.
Viroids
10.
Prokaryotes are responsible for which of these processes? (E) a.
Decomposing sewage matter b.
Fixing inorganic nitrogen c.
Refining metallic ores d.
Fermenting cheese e.
All of the above
Short Answer:
Prokaryotes have many applications in our world today. Describe three and explain why it is advantageous to use prokaryotes.







![Prokaryotes Questions[Emily Project]. - kyoussef-mci](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008946159_1-52d84b79af1cee5520579fd5edba96bf-300x300.png)