Classification study guide Name ______ date ______ Earth is 4.5
advertisement

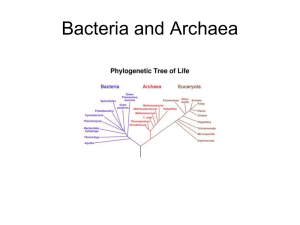
Classification study guide Name _____________ date ________ Earth is 4.5 (ish) billions years old life started 3.5 billion years ago (bya) Miller and Urey’s experiment – know how they set it up found amino acids, the building blocks of proteins other found adenine, a building block of DNA, RNA, and ATP earliest life – similar to Archaea probably Prokaryotes: Archaea and Bacteria – no nucleus Archaea – extremophiles – high salt, high temps, high pressure (deep ocean) some live in “normal” environments Next organisms were the true bacteria – shapes: cocci (round), bacilli (rod-shaped), or spiral bacteria cynaobacteria – photosynthesis – made the first free oxygen by splitting water during photosynthesis See chart that we made together domains: Arachaea, Bacteria, Eukarya Kingdoms: Archaebaceria Eubacteria Prokaryotes Domain Archaea Bacteria Kingdom Archaebacteria Eubacteria Examples? extremophiles Strep Classification study guide Eukaryotes Eukarya Protists algae Fungi mushrooms Plantae multicellular autotroph Animalia Multicellular heteroptroph Name _____________ date ________ Earth is 4.5 (ish) billions years old life started 3.5 billion years ago (bya) Miller and Urey’s experiment – know how they set it up found amino acids, the building blocks of proteins other found adenine, a building block of DNA, RNA, and ATP earliest life – similar to Archaea probably Prokaryotes: Archaea and Bacteria – no nucleus Archaea – extremophiles – high salt, high temps, high pressure (deep ocean) some live in “normal” environments Next organisms were the true bacteria – shapes: cocci (round), bacilli (rod-shaped), or spiral bacteria cynaobacteria – photosynthesis – made the first free oxygen by splitting water during photosynthesis See chart that we made together domains: Arachaea, Bacteria, Eukarya Kingdoms: Archaebaceria Eubacteria Prokaryotes Domain Archaea Bacteria Kingdom Archaebacteria Eubacteria Examples? extremophiles Strep Eukaryotes Eukarya Protists algae Fungi mushrooms Plantae multicellular autotroph Animalia Multicellular heteroptroph Know the characteristics of living things. Homeostasis – maintain stable internal environment – such as blood pressure, body temperature in mammals and birds Are viruses alive? Definition of a species – group of similar organisms breed in nature and produce fertile offspring Domain – Kingdom – Phylum – Class - Order – Family – Genus - species Linnaeus – classified animals by binomial nomenclature based on how things work Evolutionary classification – based on characteristics acquired through evolution shown by a cladogram - be able to read a cladogram Now we classify by DNA and proteins mutations occur at a steady rate (mostly) so they can be used as a molecular clock to determine how long ago two species had a common ancestor dichotomous key – used to identify organisms based on physical traits each step of the key has two possibilities – must be one or the other, cannot be both be able to use a dichotomous key What was early Earth’s atmosphere like? was there free oxygen? Know the characteristics of living things. Homeostasis – maintain stable internal environment – such as blood pressure, body temperature in mammals and birds Are viruses alive? Definition of a species – group of similar organisms breed in nature and produce fertile offspring Domain – Kingdom – Phylum – Class - Order – Family – Genus - species Linnaeus – classified animals by binomial nomenclature based on how things work Evolutionary classification – based on characteristics acquired through evolution shown by a cladogram - be able to read a cladogram Now we classify by DNA and proteins mutations occur at a steady rate (mostly) so they can be used as a molecular clock to determine how long ago two species had a common ancestor dichotomous key – used to identify organisms based on physical traits each step of the key has two possibilities – must be one or the other, cannot be both be able to use a dichotomous key What was early Earth’s atmosphere like? was there free oxygen?