Types of Microbes
advertisement

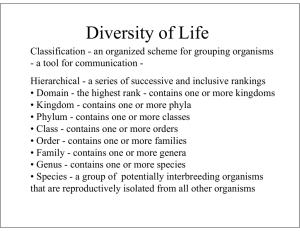
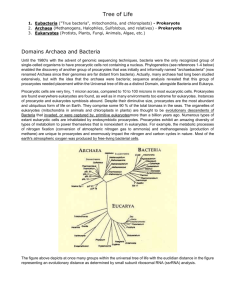
Types of Microbes JAHS Microbiology 2015 Types of Microorganisms ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Bacteria Prokaryotes: genetic material is NOT enclosed inside a nucleus Archaea Fungi Eukaryotes: Protozoa has a nucleus containing the Algae cell’s DNA Multicellular Animal Parasites Viruses Classification of Microorganisms The Three Domains of Life ● Bacteria ● Archaea ● Eukarya ○ ○ ○ ○ Protists Fungi Plants Animals The Three Domains of Life Carl R. Woese Pioneered the use of ribosomal RNA as a molecular chronometer to construct phylogenetic trees. Bacteria ● Prokaryotes ● Peptidoglycan cell walls ● Binary fission ● For energy, use organic chemicals, inorganic chemicals, or photosynthesis Bacteria There are three common bacterial shapes: ● Bacillus: rod-like ● Coccus: spherical ● Spiral: corkscrew shaped or curved Archaea ● ● ● ● Prokaryotic Lack peptidoglycan Live in extreme environments (NOT all!) Include ○ Methanogens ○ Extreme halophiles ○ Extreme thermophiles ● Not known to cause disease in humans Fungi ● Eukaryotes ● Chitin cell walls ● Use organic chemicals for energy ● Non-photosynthetic ● Some cause disease in humans Fungi ● Some are unicellular ○ Yeasts ● Some are multicellular ○ Molds and mushrooms ■ Consist of masses of mycelia - composed of filaments called hyphae. Protozoa ● Unicellular eukaryotes ● Absorb or ingest organic chemicals ● May be motile via pseudopods, cilia, or flagella ● Reproduce sexually or asexually Algae ● Eukaryotes ● Cellulose cell walls ● Use photosynthesis for energy ○ Produce molecular oxygen and organic compounds ● Reproduce sexually or asexually Viruses ● Acellular ● Consist of DNA or RNA core, surrounded by a protein coat ○ Coat may be enclosed in a lipid envelope ● Viruses are only replicated when they are in a living host cell Multicellular Animal Parasites ● Eukaryotes ● Multicellular animals ● Parasitic flatworms and roundworms are called helminths ● Microscopic stages in life cycles.