PowerPoint

The Six Kingdoms
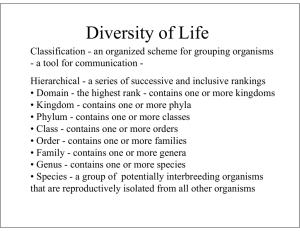
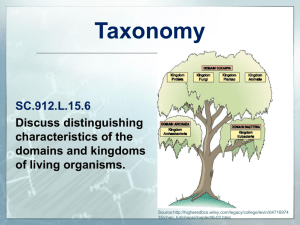
Living things will fall into one of the following kingdoms: archaebacteria, eubacteria, protists, fungi, plants, animals
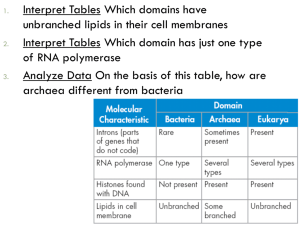
Archaebacteria
Older form of bacteria (archae = ancient)
Unicellular bacteria
Found in extreme environments
Hot springs
Deep thermal vents
Think about chemiosynthesis (anaerobic = without oxygen)
Obtain energy from inorganic (no carbon) molecules or from the light
Examples:
Halophiles
thermoacidophiles
Eubacteria
Unicellular bacteria
They have their own kingdom because their chemical make-up is different
They can be autotrophs, heterotrophs, or chemotrophs
Familiar bacteria (eu- means true)
Examples:
Streptococci (bacteria for sore throat)
Cyanobacteria (blue-green bacteria)
Saprobs (decomposers)
Protist
Sometimes referred to as the “odds and ends” because their members are different from one another
Unicellular and multicellular organisms
They represent the stepping stone between bacteria and plants/animals/fungi
Examples:
Diatoms chlorophyta (algae) (-phyto = plant)
Protozoa
sarcodina
Fungi
Multicellular complex organisms
Decompose the dead matter in the environment (nutrient cycling)
Not considered plants because they CANNOT make their own food
Examples:
Mushrooms
Mold
mildew
Plants
Multicellular organisms with complex cells
Autotrophs…make their own food (auto = self troph = feeder)
Without plants, like could not exist because they produce oxygen through photosynthesis (photo = light)
Examples:
flowering plants
Mosses
ferns
Animals
Multicellular (multi = many) organism with complex cells
Heterotrophs…they CANNOT make their own food (hetero = different troph = feeder)
Primary/Secondary/Tertiary Consumers
Herbivores
Carnivores
Scavengers
Omnivores (omni = all)
Examples:
Tiger
Bird snake